Page 474 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 474
P1: KOA
BLUK007-12 BLUK007-Kendall May 12, 2005 20:37 Char Count= 0
470 Chapter 12: Haematology and clinical immunology
alcohol, liver disease, hypothyroidism or drug induced, Megaloblastic anaemia
e.g. azathioprine. The exact mechanism is not under-
Definition
stood, but there is often an increased lipid deposition in
Megaloblastic anaemia is characterised by the presence
the membrane of the red cells.
in the bone marrow of megaloblasts and macrocytic red
blood cells.
Clinical features
Symptoms and signs of anaemia (see page 467). Aetiology
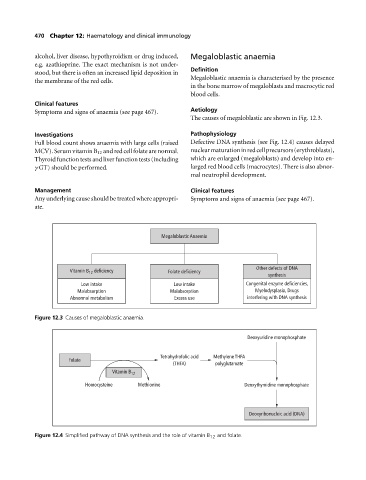
The causes of megaloblastic are shown in Fig. 12.3.
Investigations Pathophysiology
Full blood count shows anaemia with large cells (raised Defective DNA synthesis (see Fig. 12.4) causes delayed
MCV). Serum vitamin B 12 and red cell folate are normal. nuclearmaturationinredcellprecursors(erythroblasts),
Thyroid function tests and liver function tests (including which are enlarged (megaloblasts) and develop into en-
γ GT) should be performed. larged red blood cells (macrocytes). There is also abnor-
mal neutrophil development.
Management Clinical features
Any underlying cause should be treated where appropri- Symptoms and signs of anaemia (see page 467).
ate.
Megaloblastic Anaemia
Other defects of DNA
Vitamin B deficiency Folate deficiency
12
synthesis
Low intake Low intake Congenital enzyme deficiencies,
Malabsorption Malabsorption Myelodysplasia, Drugs
Abnormal metabolism Excess use interfering with DNA synthesis
Figure 12.3 Causes of megaloblastic anaemia.
Deoxyuridine monophosphate
Tetrahydrofolic acid Methylene THFA
Folate
(THFA) polyglutamate
Vitamin B 12
Homocysteine Methionine Deoxythymidine monophosphate
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Figure 12.4 Simplified pathway of DNA synthesis and the role of vitamin B 12 and folate.