Page 482 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 482
P1: KOA
BLUK007-12 BLUK007-Kendall May 12, 2005 20:37 Char Count= 0
478 Chapter 12: Haematology and clinical immunology
oxidant stress such as with infections or drugs, Aetiology
e.g. primaquine, sulphonamides, nitrofurantoin, Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia is subdivided accord-
ciprofloxacin, dapsone and naphthalene (mothballs). ing to the temperature at which the antibodies bind to
Favism is acute haemolysis following ingestion of fava the red cells:
(broad) beans. Warm autoimmune haemolytic anaemia: Antibodies
◦
bind best at 37 C
Cold autoimmune haemolytic anaemia: Antibodies
Complications
bind at lower temperatures, this type is further subdi-
Afteranoxidant shock the haemoglobin levels may fall
vided into cold haemagglutinin disease (CHAD) and
dramatically with death following unless transfused.
paroxysmal cold haemoglobinuria.
Investigations Pathophysiology
During an attack the blood film may show irregularly IgMorIgG antibodies are produced, which bind to red
contracted cells, bite cells (indented membrane), blister cells.
cells (cells in whichhaemoglobin appears detached from IgM (and IgG which fully activates complement)
the cell membrane), Heinz bodies and increased reticu- cause lysis of cells within the vessel (intravascular
locytes.BetweenattackstheG6PDlevelcanbemeasured. haemolysis).
IgGwhich only partially activate complement cause
extravascular haemolysis with opsonised red cells
Management
either completely phagocytosed in the spleen or par-
Avoid causative drugs and foods, treat infections and
tially phagocytosed leading to the formation of sphe-
transfuse as required.
rocytes.
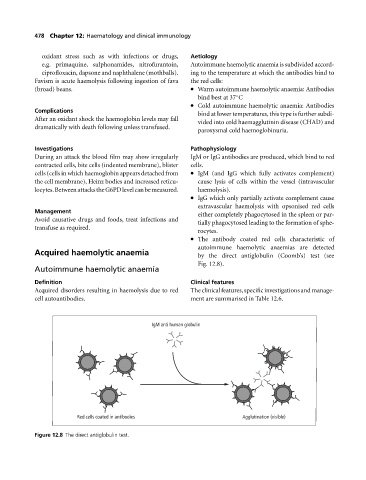
The antibody coated red cells characteristic of
autoimmune haemolytic anaemias are detected
Acquired haemolytic anaemia by the direct antiglobulin (Coomb’s) test (see
Fig. 12.8).
Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia
Definition Clinical features
Acquired disorders resulting in haemolysis due to red The clinical features, specific investigations and manage-
cell autoantibodies. ment are summarised in Table 12.6.
IgM anti human globulin
Red cells coated in antibodies Agglutination (visible)
Figure 12.8 The direct antiglobulin test.