Page 508 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 508
P1: KOA
BLUK007-12 BLUK007-Kendall May 12, 2005 20:37 Char Count= 0
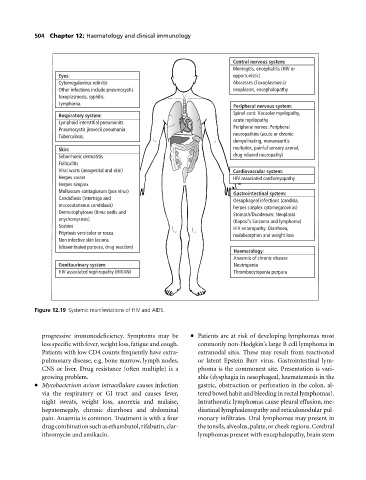
504 Chapter 12: Haematology and clinical immunology
Central nervous system:
Meningitis, encephalitis (HIV or
Eyes: opportunistic)
Cytomegalovirus retinitis Abscesses (Toxoplasmosis)
Other infections include pneumocystis neoplasms, encephalopathy
toxoplasmosis, syphilis.
Lymphoma.
Peripheral nervous system:
Spinal cord: Vacuolar myelopathy,
Respiratory system:
acute myelopathy
Lymphoid interstitial pneumonits
Peripheral nerves: Peripheral
Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia
neuropathies (acute or chronic
Tuberculosis.
demyelinating, mononeuritis
Skin: multiplex, painful sensory axonal,
Seborrhoeic dermatitis drug relaxed neuropathy)
Folliculitis
Viral warts (anogenital and skin) Cardiovascular system:
Herpes zoster HIV associated cardiomyopathy
Herpes simplex
Molluscum contagiosum (pox virus)
Gastrointestinal system:
Candidiasis (intertrigo and
Oesophageal infections (candida,
mucocutaneous candidasis)
herpes simplex cytomegalovirus)
Dermatophytoses (tinea pedis and
Stomach/Duodenum: Neoplasia
onychomycosis) (Kaposi's Sarcoma and lymphoma)
Scabies HIV enteropathy: Diarrhoea,
Pityriasis versicolor or rosea malabsorption and weight loss
Non infective skin lesions
(disseminated purpura, drug reaction)
Haematology:
Anaemia of chronic disease
Genitourinary system: Neutropenia
HIV associated nephropathy (HIVAN) Thrombocytopenia purpura
Figure 12.19 Systemic manifestations of HIV and AIDS.
progressive immunodeficiency. Symptoms may be Patients are at risk of developing lymphomas most
less specific with fever, weight loss, fatigue and cough. commonly non-Hodgkin’s large B cell lymphoma in
Patients with low CD4 counts frequently have extra- extranodal sites. These may result from reactivated
pulmonary disease, e.g. bone marrow, lymph nodes, or latent Epstein Barr virus. Gastrointestinal lym-
CNS or liver. Drug resistance (often multiple) is a phoma is the commonest site. Presentation is vari-
growing problem. able (dysphagia in oesophageal, haematemesis in the
Mycobacterium avium intracellulare causes infection gastric, obstruction or perforation in the colon, al-
via the respiratory or GI tract and causes fever, teredbowel habit and bleeding in rectal lymphomas).
night sweats, weight loss, anorexia and malaise, Intrathoratic lymphomas cause pleural effusion, me-
hepatomegaly, chronic diarrhoea and abdominal diastinal lymphadenopathy and reticulonodular pul-
pain. Anaemia is common. Treatment is with a four monary infiltrates. Oral lymphomas may present in
drugcombinationsuchasethambutol,rifabutin,clar- the tonsils, alveolus, palate, or cheek regions. Cerebral
ithromycin and amikacin. lymphomas present with encephalopathy, brain stem