Page 505 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 505
P1: KOA
BLUK007-12 BLUK007-Kendall May 12, 2005 20:37 Char Count= 0
Chapter 12: HIV 501
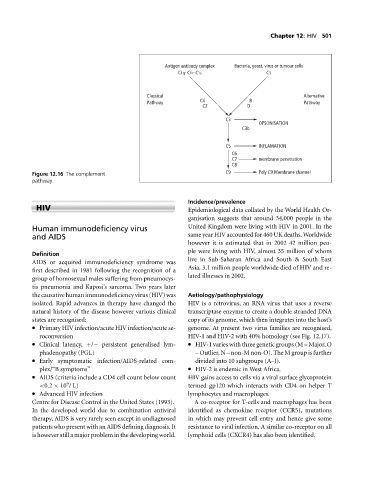
Antigen antibody complex Bacteria, yeast, virus or tumour cells
C1q- C1r- C1s C3
Classical Alternative
C4 B
Pathway Pathway
C2 D
C3
OPSONISATION
C3b
C5 INFLAMATION
C6
C7 membrane penetration
C8
Figure 12.16 The complement C9 Poly C9 Membrane channel
pathway.
Incidence/prevalence
HIV Epidemiological data collated by the World Health Or-
ganisation suggests that around 34,000 people in the
Human immunodeficiency virus United Kingdom were living with HIV in 2001. In the
and AIDS same year HIV accounted for 460 UK deaths. Worldwide
however it is estimated that in 2002 42 million peo-
ple were living with HIV, almost 35 million of whom
Definition
live in Sub-Saharan Africa and South & South East
AIDS or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome was
Asia. 3.1 million people worldwide died of HIV and re-
first described in 1981 following the recognition of a
lated illnesses in 2002.
group of homosexual males suffering from pneumocys-
tis pneumonia and Kaposi’s sarcoma. Two years later
thecausativehumanimmunodeficiencyvirus(HIV)was Aetiology/pathophysiology
isolated. Rapid advances in therapy have changed the HIV is a retrovirus, an RNA virus that uses a reverse
natural history of the disease however various clinical transcriptase enzyme to create a double stranded DNA
states are recognised: copy of its genome, which then integrates into the host’s
Primary HIV infection/acute HIV infection/acute se- genome. At present two virus families are recognised,
roconversion HIV-1 and HIV-2 with 40% homology (see Fig. 12.17).
Clinical latency, +/− persistent generalised lym- HIV-1 varies with three genetic groups (M – Major, O
phadenopathy (PGL) –Outlier, N – non-M non-O). The M group is further
Early symptomatic infection/AIDS-related com- divided into 10 subgroups (A–J).
plex/“B symptoms” HIV-2 is endemic in West Africa.
AIDS (criteria include a CD4 cell count below count HIV gains access to cells via a viral surface glycoprotein
9
<0.2 × 10 /L) termed gp120 which interacts with CD4 on helper T
Advanced HIV infection lymphocytes and macrophages.
Centre for Disease Control in the United States (1993). Aco-receptor for T-cells and macrophages has been
In the developed world due to combination antiviral identified as chemokine receptor (CCR5), mutations
therapy, AIDS is very rarely seen except in undiagnosed in which may prevent cell entry and hence give some
patients who present with an AIDS defining diagnosis. It resistance to viral infection. A similar co-receptor on all
is however still a major problem in the developing world. lymphoid cells (CXCR4) has also been identified.