Page 501 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 501
P1: KOA
BLUK007-12 BLUK007-Kendall May 12, 2005 20:37 Char Count= 0
Chapter 12: Transfusion medicine 497
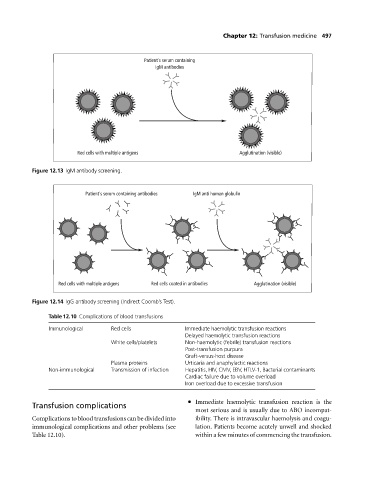
Patient's serum containing
IgM antibodies
Red cells with multiple antigens Agglutination (visible)
Figure 12.13 IgM antibody screening.
Patient's serum containing antibodies IgM anti human globulin
Red cells with multiple antigens Red cells coated in antibodies Agglutination (visible)
Figure 12.14 IgG antibody screening (Indirect Coomb’s Test).
Table 12.10 Complications of blood transfusions
Immunological Red cells Immediate haemolytic transfusion reactions
Delayed haemolytic transfusion reactions
White cells/platelets Non-haemolytic (febrile) transfusion reactions
Post-transfusion purpura
Graft-versus-host disease
Plasma proteins Urticaria and anaphylactic reactions
Non-immunological Transmission of infection Hepatitis, HIV, CMV, EBV, HTLV-1, Bacterial contaminants
Cardiac failure due to volume overload
Iron overload due to excessive transfusion
Immediate haemolytic transfusion reaction is the
Transfusion complications
most serious and is usually due to ABO incompat-
Complications to blood transfusions can be divided into ibility. There is intravascular haemolysis and coagu-
immunological complications and other problems (see lation. Patients become acutely unwell and shocked
Table 12.10). within a few minutes of commencing the transfusion.