Page 57 - VIRANSH COACHING CLASSES
P. 57
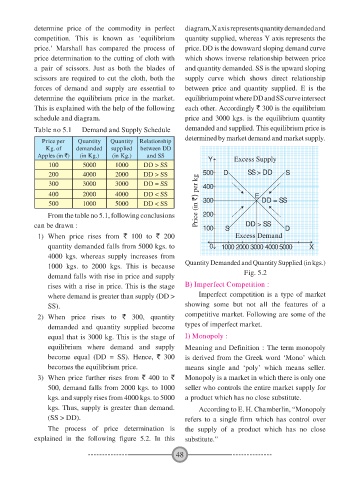
determine price of the commodity in perfect diagram, X axis represents quantity demanded and
competition. This is known as ‘equilibrium quantity supplied, whereas Y axis represents the
price.’ Marshall has compared the process of price. DD is the downward sloping demand curve
price determination to the cutting of cloth with which shows inverse relationship between price
a pair of scissors. Just as both the blades of and quantity demanded. SS is the upward sloping
scissors are required to cut the cloth, both the supply curve which shows direct relationship
forces of demand and supply are essential to between price and quantity supplied. E is the
determine the equilibrium price in the market. equilibrium point where DD and SS curve intersect
This is explained with the help of the following each other. Accordingly ` 300 is the equilibrium
schedule and diagram. price and 3000 kgs. is the equilibrium quantity
Table no 5.1 Demand and Supply Schedule demanded and supplied. This equilibrium price is
determined by market demand and market supply.
Price per Quantity Quantity Relationship
Kg. of demanded supplied between DD
Apples (in `) (in Kg.) (in Kg.) and SS
Y Excess Supply
100 5000 1000 DD > SS
200 4000 2000 DD > SS D SS > DD S
300 3000 3000 DD = SS 400
400 2000 4000 DD < SS E
300
500 1000 5000 DD < SS Price (in `) per kg 500 DD = SS
From the table no 5.1, following conclusions 200
can be drawn : DD > SS
100 S D
1) When price rises from ` 100 to ` 200 Excess Demand
quantity demanded falls from 5000 kgs. to 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 X
4000 kgs. whereas supply increases from
1000 kgs. to 2000 kgs. This is because Quantity Demanded and Quantity Supplied (in kgs.)
demand falls with rise in price and supply Fig. 5.2
rises with a rise in price. This is the stage B) Imperfect Competition :
where demand is greater than supply (DD > Imperfect competition is a type of market
SS). showing some but not all the features of a
2) When price rises to ` 300, quantity competitive market. Following are some of the
demanded and quantity supplied become types of imperfect market.
equal that is 3000 kg. This is the stage of I) Monopoly :
equilibrium where demand and supply Meaning and Definition : The term monopoly
become equal (DD = SS). Hence, ` 300 is derived from the Greek word ‘Mono’ which
becomes the equilibrium price. means single and ‘poly’ which means seller.
3) When price further rises from ` 400 to ` Monopoly is a market in which there is only one
500, demand falls from 2000 kgs. to 1000 seller who controls the entire market supply for
kgs. and supply rises from 4000 kgs. to 5000 a product which has no close substitute.
kgs. Thus, supply is greater than demand. According to E. H. Chamberlin, “Monopoly
(SS > DD). refers to a single firm which has control over
The process of price determination is the supply of a product which has no close
explained in the following figure 5.2. In this substitute.”
48