Page 117 - [Uma_Sekaran]_Research_methods_for_business__a_sk(BookZZ.org)
P. 117
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK 101
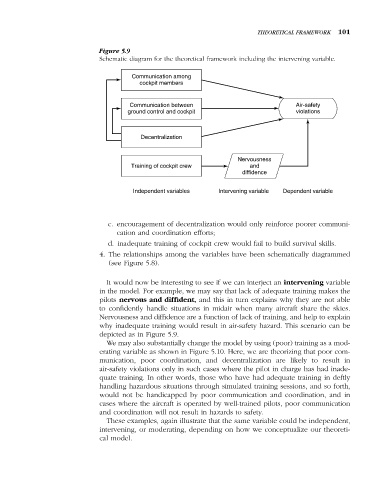
Figure 5.9
Schematic diagram for the theoretical framework including the intervening variable.
Communication among
cockpit members
Communication between Air-safety
ground control and cockpit violations
Decentralization
Nervousness
Training of cockpit crew and
diffidence
Independent variables Intervening variable Dependent variable
c. encouragement of decentralization would only reinforce poorer communi-
cation and coordination efforts;
d. inadequate training of cockpit crew would fail to build survival skills.
4. The relationships among the variables have been schematically diagrammed
(see Figure 5.8).
It would now be interesting to see if we can interject an intervening variable
in the model. For example, we may say that lack of adequate training makes the
pilots nervous and diffident, and this in turn explains why they are not able
to confidently handle situations in midair when many aircraft share the skies.
Nervousness and diffidence are a function of lack of training, and help to explain
why inadequate training would result in air-safety hazard. This scenario can be
depicted as in Figure 5.9.
We may also substantially change the model by using (poor) training as a mod-
erating variable as shown in Figure 5.10. Here, we are theorizing that poor com-
munication, poor coordination, and decentralization are likely to result in
air-safety violations only in such cases where the pilot in charge has had inade-
quate training. In other words, those who have had adequate training in deftly
handling hazardous situations through simulated training sessions, and so forth,
would not be handicapped by poor communication and coordination, and in
cases where the aircraft is operated by well-trained pilots, poor communication
and coordination will not result in hazards to safety.
These examples, again illustrate that the same variable could be independent,
intervening, or moderating, depending on how we conceptualize our theoreti-
cal model.