Page 7 - PR 2014 2016 07 Nuclear Science and Technology
P. 7
Nuclear Science and Technology | Progress Report 149
Materials which have been investigated are:
1 Oxide semiconductors: new families of semiconductors, which
are doped with magnetic materials in order to use the elec-
tron spin information, are under intensive investigation as
they can be used for spintronics. Effects of doping in ZnO,
In O , SnO , TiO , and vanadium oxides are being investigat-
2 3 2 2
ed by PAC in order to understand the local crystalline struc-
ture around the dopant and the its electronic structure.
2 Insulator oxides with large bandgap as HfO , ZrO and CeO
2
2
2
are promising materials to replace SiO as a gate dielectric to
2
prevent leakage current in complementary metal oxide semi-
conductor (CMOS) transistors. Thin films and nano-structured
powders of these materials are under investigation using PAC
spectroscopy in order to obtain an atomic scale characteri-
zation of their properties under different temperatures.
3 Rare-earth based compounds: series of intermetallic compounds
based on rare earth elements show different magnetic behaviors
and exhibit very interesting physical phenomena like Fermi liquid
behavior, Kondo effect, etc. These properties are not well under-
stood yet, and nuclear techniques are very suitable to investigate
the microscopic origin of such phenomena. In our laboratory,
we have studied heavy fermions compounds such as REIn (RE
3
= rare-earth element), REMn X (RE= rare-earth, X = Si, Ge) and
2 2
LaMnSi with PAC technique using Ce and Cd probe nuclei.
140
111
2
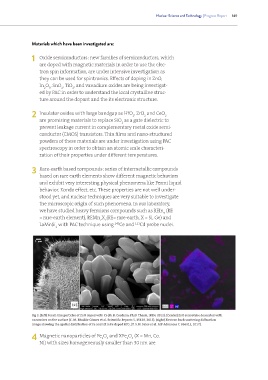
Fig 3. (left) Pencil-like particles of ZnO doped with Cr (M. R. Cordeiro, Ph.D. Thesis, IPEN, 2012). (Center) ZnO microtube decorated with
nanowires on the surface (C. M. Rivaldo-Gómez et al. Scientific Reports 5, 15128, 2015). (right) Electron back scattering diffraction
image showing the spatial distribution of Fe and Hf in Fe doped HfO (T. S. N. Sales et al. AIP Advances 7, 056315, 2017).
2
4 Magnetic nanoparticles of Fe O and XFe O (X = Mn, Co,
3
4
4
2
Ni) with sizes homogeneously smaller than 30 nm are