Page 25 - Cardiac Electrophysiology | A Modeling and Imaging Approach
P. 25
P. 25
depend on channel accumulation in the open sate (the traditionally accepted mechanism) is a
consequence of the two-stage voltage sensor transitions. It was confirmed by action-potential
clamp experiments that showed
rapid increase of I current at
Ks
fast rate, with very little
instantaneous current (indicative
of minimal open-state
accumulation) at action potential
onset.
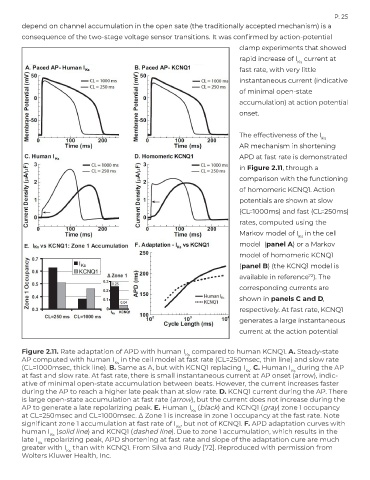
The effectiveness of the I
Ks
AR mechanism in shortening
APD at fast rate is demonstrated
in Figure 2.11, through a
comparison with the functioning
of homomeric KCNQ1. Action
potentials are shown at slow
(CL=1000ms) and fast (CL=250ms)
rates, computed using the
Markov model of I in the cell
Ks
model (panel A) or a Markov
model of homomeric KCNQ1
(panel B) (the KCNQ1 model is
available in reference ). The
72
corresponding currents are
shown in panels C and D,
respectively. At fast rate, KCNQ1
generates a large instantaneous
current at the action potential
Figure 2.11. Rate adaptation of APD with human I compared to human KCNQ1. A. Steady-state
Ks
AP computed with human I in the cell model at fast rate (CL=250msec, thin line) and slow rate
Ks
(CL=1000msec, thick line). B. Same as A, but with KCNQ1 replacing I . C. Human I during the AP
Ks
Ks
at fast and slow rate. At fast rate, there is small instantaneous current at AP onset (arrow), indic-
ative of minimal open-state accumulation between beats. However, the current increases faster
during the AP to reach a higher late peak than at slow rate. D. KCNQ1 current during the AP. There
is large open-state accumulation at fast rate (arrow), but the current does not increase during the
AP to generate a late repolarizing peak. E. Human I (black) and KCNQ1 (gray) zone 1 occupancy
Ks
at CL=250msec and CL=1000msec. ∆ Zone 1 is increase in zone 1 occupancy at the fast rate. Note
significant zone 1 accumulation at fast rate of I , but not of KCNQ1. F. APD adaptation curves with
Ks
human I (solid line) and KCNQ1 (dashed line). Due to zone 1 accumulation, which results in the
Ks
late I repolarizing peak, APD shortening at fast rate and slope of the adaptation cure are much
Ks
greater with I than with KCNQ1. From Silva and Rudy [72]. Reproduced with permission from
Ks
Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.