Page 21 - Cardiac Electrophysiology | A Modeling and Imaging Approach
P. 21
P. 21
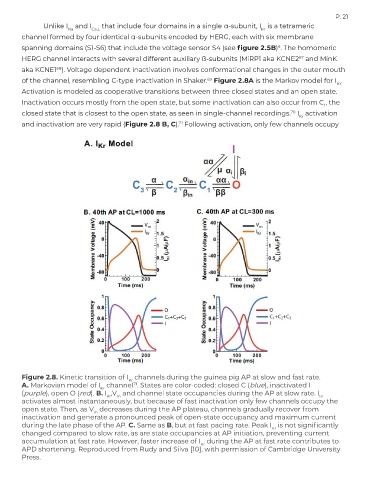
Unlike I and I Ca,L that include four domains in a single α-subunit, I is a tetrameric
Na
Kr
channel formed by four identical α-subunits encoded by HERG, each with six membrane
spanning domains (S1-S6) that include the voltage sensor S4 (see figure 2.5B) . The homomeric
9
HERG channel interacts with several different auxiliary ß-subunits (MiRP1 aka KCNE2 and MinK
67
aka KCNE1 ). Voltage dependent inactivation involves conformational changes in the outer mouth
68
of the channel, resembling C-type inactivation in Shaker. Figure 2.8A is the Markov model for I .
69
Kr
Activation is modeled as cooperative transitions between three closed states and an open state.
Inactivation occurs mostly from the open state, but some inactivation can also occur from C , the
1
closed state that is closest to the open state, as seen in single-channel recordings. I activation
70
Kr
and inactivation are very rapid (Figure 2.8 B, C). Following activation, only few channels occupy
71
Figure 2.8. Kinetic transition of I channels during the guinea pig AP at slow and fast rate.
Kr
A. Markovian model of I channel . States are color-coded: closed C (blue), inactivated I
71
Kr
(purple), open O (red). B. I ,V and channel state occupancies during the AP at slow rate. I
Kr
Kr
m
activates almost instantaneously, but because of fast inactivation only few channels occupy the
open state. Then, as V decreases during the AP plateau, channels gradually recover from
m
inactivation and generate a pronounced peak of open-state occupancy and maximum current
during the late phase of the AP. C. Same as B, but at fast pacing rate. Peak I is not significantly
Kr
changed compared to slow rate, as are state occupancies at AP initiation, preventing current
accumulation at fast rate. However, faster increase of I during the AP at fast rate contributes to
Kr
APD shortening. Reproduced from Rudy and Silva [10], with permission of Cambridge University
Press.