Page 17 - Cardiac Electrophysiology | A Modeling and Imaging Approach
P. 17
P. 17
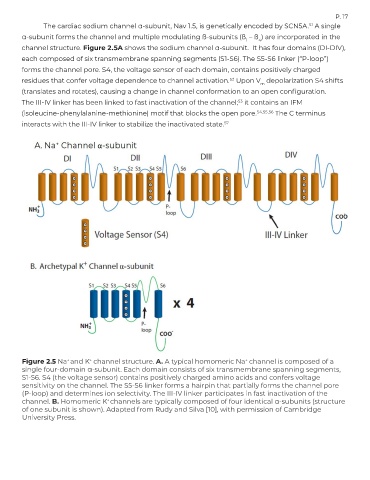
The cardiac sodium channel α-subunit, Nav 1.5, is genetically encoded by SCN5A. A single
51
α-subunit forms the channel and multiple modulating ß-subunits (ß – ß ) are incorporated in the
4
1
channel structure. Figure 2.5A shows the sodium channel α-subunit. It has four domains (DI-DIV),
each composed of six transmembrane spanning segments (S1-S6). The S5-S6 linker (“P-loop”)
forms the channel pore. S4, the voltage sensor of each domain, contains positively charged
residues that confer voltage dependence to channel activation. Upon V depolarization S4 shifts
52
m
(translates and rotates), causing a change in channel conformation to an open configuration.
The III-IV linker has been linked to fast inactivation of the channel; it contains an IFM
53
(isoleucine-phenylalanine-methionine) motif that blocks the open pore. 54,55,56 The C terminus
interacts with the III-IV linker to stabilize the inactivated state. 57
Figure 2.5 Na and K channel structure. A. A typical homomeric Na channel is composed of a
+
+
+
single four-domain α-subunit. Each domain consists of six transmembrane spanning segments,
S1-S6. S4 (the voltage sensor) contains positively charged amino acids and confers voltage
sensitivity on the channel. The S5-S6 linker forms a hairpin that partially forms the channel pore
(P-loop) and determines ion selectivity. The III-IV linker participates in fast inactivation of the
channel. B. Homomeric K channels are typically composed of four identical α-subunits (structure
+
of one subunit is shown). Adapted from Rudy and Silva [10], with permission of Cambridge
University Press.