Page 20 - Cardiac Electrophysiology | A Modeling and Imaging Approach
P. 20
P. 20
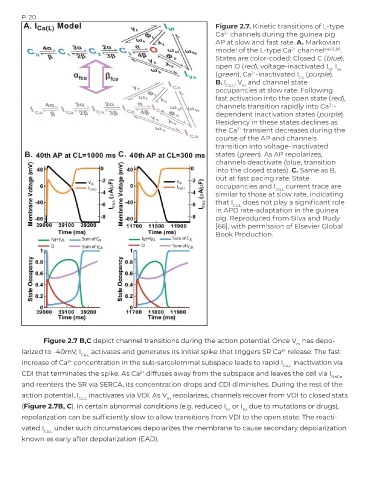
Figure 2.7. Kinetic transitions of L-type
Ca channels during the guinea pig
2+
AP at slow and fast rate. A. Markovian
model of the L-type Ca channel 64,65,66 .
2+
States are color-coded: Closed C (blue),
open O (red), voltage-inactivated I I
Vf, Vs
(green), Ca -inactivated I (purple).
2+
Ca
B. I Ca,L , V and channel state
m
occupancies at slow rate. Following
fast activation into the open state (red),
channels transition rapidly into Ca -
2+
dependent inactivation states (purple).
Residency in these states declines as
the Ca transient decreases during the
2+
course of the AP and channels
transition into voltage-inactivated
states (green). As AP repolarizes,
channels deactivate (blue, transition
into the closed states). C. Same as B,
but at fast pacing rate. State
occupancies and I Ca,L current trace are
similar to those at slow rate, indicating
that I Ca,L does not play a significant role
in APD rate-adaptation in the guinea
pig. Reproduced from Silva and Rudy
[66], with permission of Elsevier Global
Book Production.
Figure 2.7 B,C depict channel transitions during the action potential. Once V has depo-
m
larized to -40mV, I activates and generates its initial spike that triggers SR Ca release. The fast
2+
Ca,L
increase of Ca concentration in the sub-sarcolemmal subspace leads to rapid I inactivation via
2+
Ca,L
CDI that terminates the spike. As Ca diffuses away from the subspace and leaves the cell via I
2+
NaCa
and reenters the SR via SERCA, its concentration drops and CDI diminishes. During the rest of the
action potential, I inactivates via VDI. As V repolarizes, channels recover from VDI to closed stats
Ca,L m
(Figure 2.7B, C). In certain abnormal conditions (e.g. reduced I or I due to mutations or drugs),
Kr Ks
repolarization can be sufficiently slow to allow transitions from VDI to the open state. The reacti-
vated I under such circumstances depolarizes the membrane to cause secondary depolarization
Ca,L
known as early after depolarization (EAD).