Page 616 - COSO Guidance
P. 616
3. Performance for ESG-related risks
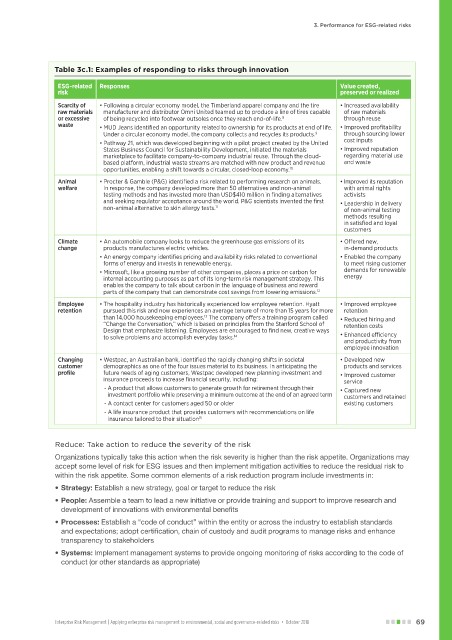
Table 3c.1: Examples of responding to risks through innovation
ESG-related Responses Value created,
risk preserved or realized
Scarcity of • Following a circular economy model, the Timberland apparel company and the tire • Increased availability
raw materials manufacturer and distributor Omni United teamed up to produce a line of tires capable of raw materials
or excessive of being recycled into footwear outsoles once they reach end-of-life. through reuse
8
waste • MUD Jeans identified an opportunity related to ownership for its products at end of life. • Improved profitability
Under a circular economy model, the company collects and recycles its products. through sourcing lower
9
• Pathway 21, which was developed beginning with a pilot project created by the United cost inputs
States Business Council for Sustainability Development, initiated the materials • Improved reputation
marketplace to facilitate company-to-company industrial reuse. Through the cloud- regarding material use
based platform, industrial waste streams are matched with new product and revenue and waste
opportunities, enabling a shift towards a circular, closed-loop economy. 10
Animal • Procter & Gamble (P&G) identified a risk related to performing research on animals. • Improved its reputation
welfare In response, the company developed more than 50 alternatives and non-animal with animal rights
testing methods and has invested more than USD$410 million in finding alternatives activists
and seeking regulator acceptance around the world. P&G scientists invented the first • Leadership in delivery
non-animal alternative to skin allergy tests. of non-animal testing
11
methods resulting
in satisfied and loyal
customers
Climate • An automobile company looks to reduce the greenhouse gas emissions of its • Offered new,
change products manufactures electric vehicles. in-demand products
• An energy company identifies pricing and availability risks related to conventional • Enabled the company
forms of energy and invests in renewable energy. to meet rising customer
• Microsoft, like a growing number of other companies, places a price on carbon for demands for renewable
internal accounting purposes as part of its long-term risk management strategy. This energy
enables the company to talk about carbon in the language of business and reward
parts of the company that can demonstrate cost savings from lowering emissions. 12
Employee • The hospitality industry has historically experienced low employee retention. Hyatt • Improved employee
retention pursued this risk and now experiences an average tenure of more than 15 years for more retention
than 14,000 housekeeping employees. The company offers a training program called • Reduced hiring and
13
“Change the Conversation,” which is based on principles from the Stanford School of retention costs
Design that emphasize listening. Employees are encouraged to find new, creative ways
14
to solve problems and accomplish everyday tasks. • Enhanced efficiency
and productivity from
employee innovation
Changing • Westpac, an Australian bank, identified the rapidly changing shifts in societal • Developed new
customer demographics as one of the four issues material to its business. In anticipating the products and services
profile future needs of aging customers, Westpac developed new planning investment and • Improved customer
insurance proceeds to increase financial security, including: service
- A product that allows customers to generate growth for retirement through their • Captured new
investment portfolio while preserving a minimum outcome at the end of an agreed term customers and retained
- A contact center for customers aged 50 or older existing customers
- A life insurance product that provides customers with recommendations on life
insurance tailored to their situation 15
Reduce: Take action to reduce the severity of the risk
Organizations typically take this action when the risk severity is higher than the risk appetite. Organizations may
accept some level of risk for ESG issues and then implement mitigation activities to reduce the residual risk to
within the risk appetite. Some common elements of a risk reduction program include investments in:
• Strategy: Establish a new strategy, goal or target to reduce the risk
• People: Assemble a team to lead a new initiative or provide training and support to improve research and
development of innovations with environmental benefits
• Processes: Establish a “code of conduct” within the entity or across the industry to establish standards
and expectations; adopt certification, chain of custody and audit programs to manage risks and enhance
transparency to stakeholders
• Systems: Implement management systems to provide ongoing monitoring of risks according to the code of
conduct (or other standards as appropriate)
Enterprise Risk Management | Applying enterprise risk management to environmental, social and governance-related risks • October 2018 69