Page 645 - ACFE Fraud Reports 2009_2020
P. 645
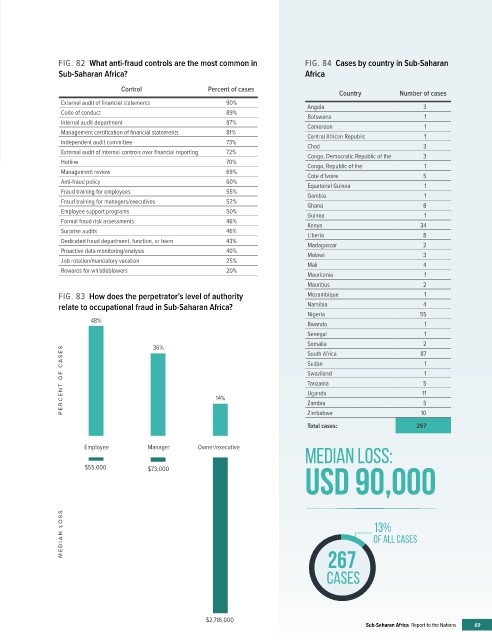
FIG. 82 What anti-fraud controls are the most common in FIG. 84 Cases by country in Sub-Saharan
Sub-Saharan Africa? Africa
Control Percent of cases
Country Number of cases
External audit of financial statements 90%
Angola 3
Code of conduct 89%
Botswana 1
Internal audit department 87%
Cameroon 1
Management certification of financial statements 81% Central African Republic 1
Independent audit committee 73% Chad 3
External audit of internal controls over financial reporting 72% Congo, Democratic Republic of the 3
Hotline 70% Congo, Republic of the 1
Management review 69% Cote d’Ivoire 5
Anti-fraud policy 60% Equatorial Guinea 1
Fraud training for employees 55%
Gambia 1
Fraud training for managers/executives 52%
Ghana 8
Employee support programs 50%
Guinea 1
Formal fraud risk assessments 46%
Kenya 34
Surprise audits 46%
Liberia 8
Dedicated fraud department, function, or team 43%
Madagascar 2
Proactive data monitoring/analysis 40%
Malawi 3
Job rotation/mandatory vacation 25% Mali 4
Rewards for whistleblowers 20%
Mauritania 1
Mauritius 2
FIG. 83 How does the perpetrator’s level of authority Mozambique 1
relate to occupational fraud in Sub-Saharan Africa? Namibia 4
Nigeria 55
48%
Rwanda 1
Senegal 1
Somalia 2
36% South Africa 87 1
PERCENT OF C A SES 14% Swaziland 11 5 5 1
Sudan
Tanzania
Uganda
Zambia
Zimbabwe
10
Total cases: 267
Employee Manager Owner/executive
MEDIAN LOSS:
usd 90,000
$55,000 $73,000
� � � � �
MEDIAN L OSS 13%
OF ALL CASES
267
CASES
$2,716,000
Sub-Saharan Africa Report to the Nations 69