Page 7 - Pharma GIT L1
P. 7
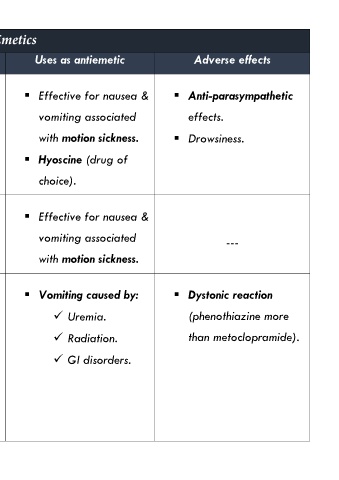
Drug Antiemetic mechanism Uses as antiemetic Adverse effects
1. Muscarinic blockers: They block M1 receptors Effective for nausea & Anti-parasympathetic
Scopolamine in vestibulo-cerebellar vomiting associated effects.
(hyoscine). pathway. with motion sickness. Drowsiness.
Hyoscine (drug of
choice).
2. H1 blockers: They block H1 receptors Effective for nausea &
Diphenhydramine. in vestibulo-cerebellar vomiting associated ---
Cyclizine. pathway. with motion sickness.
3. D2 antagonists: They block D2 receptors Vomiting caused by: Dystonic reaction
Metoclopramide. in CTZ. Uremia. (phenothiazine more
Domperidone.
Phenothiazines Radiation. than metoclopramide).
Phenothiazines.
(thiethylperazine & GI disorders.
promethazine) also
block H1 receptors.