Page 24 - Personal Study Notes (Engineering Metrology - 22342)
P. 24
Page 24 of 176
3. For taking accurate measurement of deformation such as intension and compression.
4. To determine positional errors of surfaces such as parallelism, squareness and
alignment.
5. To check the alignment of lathe centers by using suitable accurate bar between the
centers.
6. To check trueness of milling machine arbours and to check the parallelism of shaper
arm with table surface or vice.
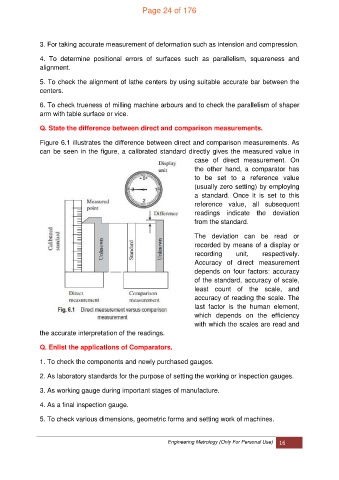
Q. State the difference between direct and comparison measurements.
Figure 6.1 illustrates the difference between direct and comparison measurements. As
can be seen in the figure, a calibrated standard directly gives the measured value in
case of direct measurement. On
the other hand, a comparator has
to be set to a reference value
(usually zero setting) by employing
a standard. Once it is set to this
reference value, all subsequent
readings indicate the deviation
from the standard.
The deviation can be read or
recorded by means of a display or
recording unit, respectively.
Accuracy of direct measurement
depends on four factors: accuracy
of the standard, accuracy of scale,
least count of the scale, and
accuracy of reading the scale. The
last factor is the human element,
which depends on the efficiency
with which the scales are read and
the accurate interpretation of the readings.
Q. Enlist the applications of Comparators.
1. To check the components and newly purchased gauges.
2. As laboratory standards for the purpose of setting the working or inspection gauges.
3. As working gauge during important stages of manufacture.
4. As a final inspection gauge.
5. To check various dimensions, geometric forms and setting work of machines.
Engineering Metrology (Only For Personal Use) 16