Page 57 - Current techniques in canine and feline neurosurgery_2017_Neat
P. 57
Chapter 4: Advanced Imaging: Intracranial Surgery 49
A
B
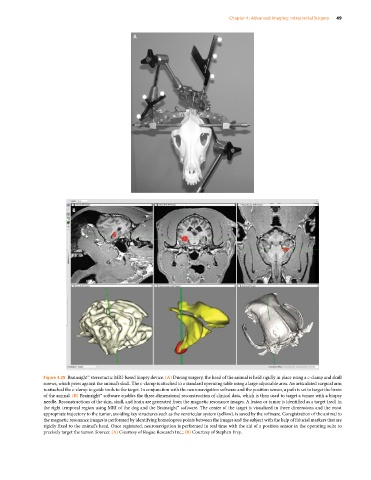
Figure 4.25 Brainsight™ stereotactic MRI‐based biopsy device. (A) During surgery, the head of the animal is held rigidly in place using a c‐clamp and skull
screws, which press against the animal’s skull. The c‐clamp is attached to a standard operating table using a large adjustable arm. An articulated surgical arm
is attached the c‐clamp to guide tools to the target. In conjunction with the neuronavigation software and the position sensor, a path is set to target the brain
of the animal. (B) Brainsight™ software enables the three‐dimensional reconstruction of clinical data, which is then used to target a tumor with a biopsy
needle. Reconstructions of the skin, skull, and brain are generated from the magnetic resonance images. A lesion or tumor is identified as a target (red) in
the right temporal region using MRI of the dog and the Brainsight™ software. The center of the target is visualized in three dimensions and the most
appropriate trajectory to the tumor, avoiding key structures such as the ventricular system (yellow), is saved by the software. Coregistration of the animal to
the magnetic resonance images is performed by identifying homologous points between the images and the subject with the help of fiducial markers that are
rigidly fixed to the animal’s head. Once registered, neuronavigation is performed in real time with the aid of a position sensor in the operating suite to
precisely target the tumor. Sources: (A) Courtesy of Rogue Research Inc.; (B) Courtesy of Stephen Frey.