Page 55 - Current techniques in canine and feline neurosurgery_2017_Neat
P. 55
Chapter 4: Advanced Imaging: Intracranial Surgery 47
A
D
B
E
C
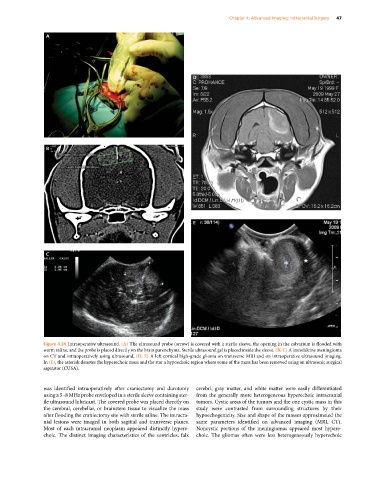
Figure 4.24 Intraoperative ultrasound. (A) The ultrasound probe (arrow) is covered with a sterile sleeve, the opening in the calvarium is flooded with
warm saline, and the probe is placed directly on the brain parenchyma. Sterile ultrasound gel is placed inside the sleeve. (B, C) A transfalcine meningioma
on CT and intraoperatively using ultrasound. (D, E) A left cortical high‐grade glioma on transverse MRI and on intraoperative ultrasound imaging.
In (E), the asterisk denotes the hyperechoic mass and the star a hypoechoic region where some of the mass has been removed using an ultrasonic surgical
aspirator (CUSA).
was identified intraoperatively after craniectomy and durotomy cerebri, gray matter, and white matter were easily differentiated
using a 5–8 MHz probe enveloped in a sterile sleeve containing ster- from the generally more heterogeneous hyperechoic intracranial
ile ultrasound lubricant. The covered probe was placed directly on tumors. Cystic areas of the tumors and the one cystic mass in this
the cerebral, cerebellar, or brainstem tissue to visualize the mass study were contrasted from surrounding structures by their
after flooding the craniectomy site with sterile saline. The intracra- hypoechogenicity. Size and shape of the masses approximated the
nial lesions were imaged in both sagittal and transverse planes. same parameters identified on advanced imaging (MRI, CT).
Most of each intracranial neoplasm appeared distinctly hypere- Noncystic portions of the meningiomas appeared most hypere-
choic. The distinct imaging characteristics of the ventricles, falx choic. The gliomas often were less heterogeneously hyperechoic