Page 1356 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 1356
The foal 1331
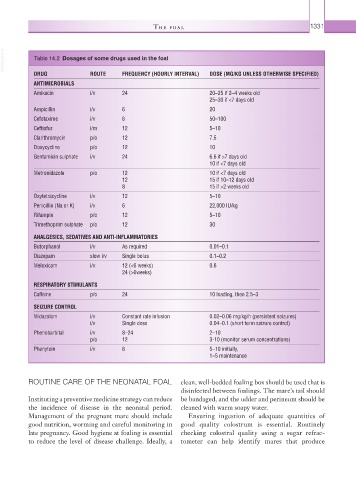
VetBooks.ir Table 14.2 Dosages of some drugs used in the foal
DRUG ROUTE FREQUENCY (HOURLY INTERVAL) DOSE (MG/KG UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED)
ANTIMICROBIALS
Amikacin i/v 24 20–25 if 2–4 weeks old
25–30 if <7 days old
Ampicillin i/v 6 20
Cefotaxime i/v 6 50–100
Ceftiofur i/m 12 5–10
Clarithromycin p/o 12 7.5
Doxycycline p/o 12 10
Gentamicin sulphate i/v 24 6.6 if >7 days old
10 if <7 days old
Metronidazole p/o 12 10 if <7 days old
12 15 if 10–12 days old
8 15 if >2 weeks old
Oxytetracycline i/v 12 5–10
Penicillin (Na or K) i/v 6 22,000 IU/kg
Rifampin p/o 12 5–10
Trimethoprim sulphate p/o 12 30
ANALGESICS, SEDATIVES AND ANTI-INFLAMMATORIES
Butorphanol i/v As required 0.01–0.1
Diazepam slow i/v Single bolus 0.1–0.2
Meloxicam i/v 12 (<6 weeks) 0.6
24 (>6weeks)
RESPIRATORY STIMULANTS
Caffeine p/o 24 10 loading, then 2.5–3
SEIZURE CONTROL
Midazolam i/v Constant rate infusion 0.02–0.06 mg/kg/h (persistent seizures)
i/v Single dose 0.04–0.1 (short term seizure control)
Phenobarbital i/v 8–24 2–10
p/o 12 3-10 (monitor serum concentrations)
Phenytoin i/v 6 5–10 initially,
1–5 maintenance
ROUTINE CARE OF THE NEONATAL FOAL clean, well-bedded foaling box should be used that is
disinfected between foalings. The mare’s tail should
Instituting a preventive medicine strategy can reduce be bandaged, and the udder and perineum should be
the incidence of disease in the neonatal period. cleaned with warm soapy water.
Management of the pregnant mare should include Ensuring ingestion of adequate quantities of
good nutrition, worming and careful monitoring in good quality colostrum is essential. Routinely
late pregnancy. Good hygiene at foaling is essential checking colostral quality using a sugar refrac-
to reduce the level of disease challenge. Ideally, a tometer can help identify mares that produce