Page 653 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 653
628 CHAPTER 3
VetBooks.ir Differential diagnosis sprays of antibiotics and anti-inflammatories and
pasture rest. Grade 4 cases have been treated surgi-
The differential diagnosis includes all the other
cally by some clinicians with topical trichloroacetic
causes of respiratory noise.
acid, electrocautery, cryotherapy and transendo-
Diagnosis scopic laser. Excessive removal of tissue has led to
Endoscopic examination is diagnostic, and a grading pharyngeal cicatrix formation.
system has been established:
Prognosis
• Grade 1: occasional small white focal spots on Prognosis is very good as the condition usually spon-
the dorsal pharyngeal wall. taneously resolves with time.
• Grade 2: multiple raised nodules on the dorsal
and lateral pharyngeal walls. FOREIGN BODIES OF THE PHARYNX
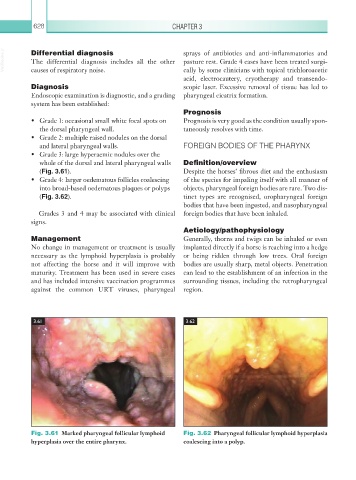
• Grade 3: large hyperaemic nodules over the
whole of the dorsal and lateral pharyngeal walls Definition/overview
(Fig. 3.61). Despite the horses’ fibrous diet and the enthusiasm
• Grade 4: larger oedematous follicles coalescing of the species for impaling itself with all manner of
into broad-based oedematous plaques or polyps objects, pharyngeal foreign bodies are rare. Two dis-
(Fig. 3.62). tinct types are recognised, oropharyngeal foreign
bodies that have been ingested, and nasopharyngeal
Grades 3 and 4 may be associated with clinical foreign bodies that have been inhaled.
signs.
Aetiology/pathophysiology
Management Generally, thorns and twigs can be inhaled or even
No change in management or treatment is usually implanted directly if a horse is reaching into a hedge
necessary as the lymphoid hyperplasia is probably or being ridden through low trees. Oral foreign
not affecting the horse and it will improve with bodies are usually sharp, metal objects. Penetration
maturity. Treatment has been used in severe cases can lead to the establishment of an infection in the
and has included intensive vaccination programmes surrounding tissues, including the retropharyngeal
against the common URT viruses, pharyngeal region.
3.61 3.62
Fig. 3.61 Marked pharyngeal follicular lymphoid Fig. 3.62 Pharyngeal follicular lymphoid hyperplasia
hyperplasia over the entire pharynx. coalescing into a polyp.