Page 449 - Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Disorders in Small Animal Practice
P. 449
Fluid and Electrolyte Disturbances In Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Disease 437
Peptides
K+ ATPase H+ Digested proteins Luminal acid
+ +
Protein kinase
Ca Ca
G cell Somatostatin
Adenyl
cyclase Gastrin Gastrin – D cell
ACh
H2 + PGE – +
–
+
+ +
+ GRP +
Histamine +
Cytokines Vagus
+
ECL cell
Vagus
– +
–
Somatostatin
D cell
Fundus Pylorus
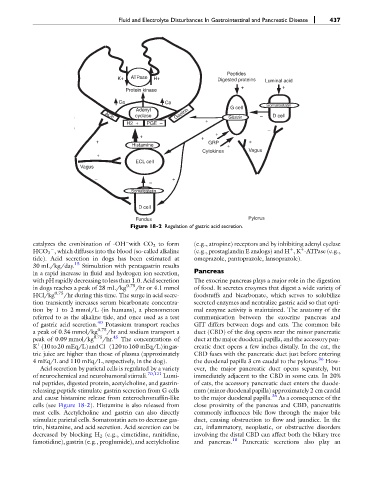
Figure 18-2 Regulation of gastric acid secretion.
catalyzes the combination of -OH with CO 2 to form (e.g., atropine) receptors and by inhibiting adenyl cyclase
þ
þ
HCO 3 , which diffuses into the blood (so-called alkaline (e.g., prostaglandin E analogs) and H ,K -ATPase (e.g.,
tide). Acid secretion in dogs has been estimated at omeprazole, pantoprazole, lansoprazole).
30 mL/kg/day. 15 Stimulation with pentagastrin results
in a rapid increase in fluid and hydrogen ion secretion, Pancreas
with pH rapidly decreasing to less than 1.0. Acid secretion The exocrine pancreas plays a major role in the digestion
in dogs reaches a peak of 28 mL/kg 0.75 /hr or 4.1 mmol of food. It secretes enzymes that digest a wide variety of
0.75
HCl/kg /hr during this time. The surge in acid secre- foodstuffs and bicarbonate, which serves to solubilize
tion transiently increases serum bicarbonate concentra- secreted enzymes and neutralize gastric acid so that opti-
tion by 1 to 2 mmol/L (in humans), a phenomenon mal enzyme activity is maintained. The anatomy of the
referred to as the alkaline tide, and once used as a test communication between the exocrine pancreas and
of gastric acid secretion. 40 Potassium transport reaches GIT differs between dogs and cats. The common bile
a peak of 0.34 mmol/kg 0.75 /hr and sodium transport a duct (CBD) of the dog opens near the minor pancreatic
peak of 0.09 mmol/kg 0.75 /hr. 45 The concentrations of duct at the major duodenal papilla, and the accessory pan-
þ
K (10to20 mEq/L)andCl (120to160 mEq/L)ingas- creatic duct opens a few inches distally. In the cat, the
tric juice are higher than those of plasma (approximately CBD fuses with the pancreatic duct just before entering
4 mEq/L and 110 mEq/L, respectively, in the dog). the duodenal papilla 3 cm caudal to the pylorus. 36 How-
Acid secretion by parietal cells is regulated by a variety ever, the major pancreatic duct opens separately, but
of neurochemical and neurohumoral stimuli. 70,121 Lumi- immediately adjacent to the CBD in some cats. In 20%
nal peptides, digested protein, acetylcholine, and gastrin- of cats, the accessory pancreatic duct enters the duode-
releasing peptide stimulate gastrin secretion from G cells num (minor duodenal papilla) approximately 2 cm caudal
and cause histamine release from enterochromaffin-like to the major duodenal papilla. 36 As a consequence of the
cells (see Figure 18-2). Histamine is also released from close proximity of the pancreas and CBD, pancreatitis
mast cells. Acetylcholine and gastrin can also directly commonly influences bile flow through the major bile
stimulate parietal cells. Somatostatin acts to decrease gas- duct, causing obstruction to flow and jaundice. In the
trin, histamine, and acid secretion. Acid secretion can be cat, inflammatory, neoplastic, or obstructive disorders
decreased by blocking H 2 (e.g., cimetidine, ranitidine, involving the distal CBD can affect both the biliary tree
famotidine), gastrin (e.g., proglumide), and acetylcholine and pancreas. 18 Pancreatic secretions also play an