Page 450 - Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Disorders in Small Animal Practice
P. 450
438 FLUID THERAPY
important role in the absorption of cobalamin (vitamin Cl across the luminal membrane. 40,89 Under maximal
B 12 ) and in the regulation of the bacterial flora of the stimulation, some secreted HCO 3 seems to enter the
small intestine, and they directly influence small intestinal lumen directly via the CFTR channel as well as by Cl /
function by modifying certain enzymes on the intestinal HCO 3 exchange. 89 The electrolyte composition of pan-
brush border and exerting trophic effects on the mucosa. creatic secretion changes in response to stimulation.
Histologically, the pancreas is composed of many At low rates of secretion, the chloride concentration
secretory lobules that contain acinar cells. These secretory exceeds that of bicarbonate, whereas at higher rates,
acini are drained by a branching ductular system that is the bicarbonate concentration is higher than the chloride
lined by a variety of epithelial cells. A dense network of concentration (Figure 18-4). Entry of acid gastric
capillaries, nerves, and lymphatics surround the acini secretions into the duodenum signals the pancreas to
and ducts. secrete its alkaline solution into the gut. 40 In the
Pancreatic acinar cells are responsible for the synthesis stimulated cat pancreas, the HCO 3 concentration
of digestive enzymes, whereas the cells lining the ductular increases from 70 to 145 mEq/ L and the Cl concentra-
system are the major source of fluid and electrolyte secre- tion decreases from 100 to 30 mEq/L. Concentrations
tion. Entry of the acid gastric secretions into the duode- of Na and K in pancreatic secretions are similar to those
þ
þ
num signals the pancreas to secrete bicarbonate into the of plasma. The concentrations of electrolytes also change
gut. The anion transporter primarily responsible for this within the pancreatic ductular system. A decrease in Cl
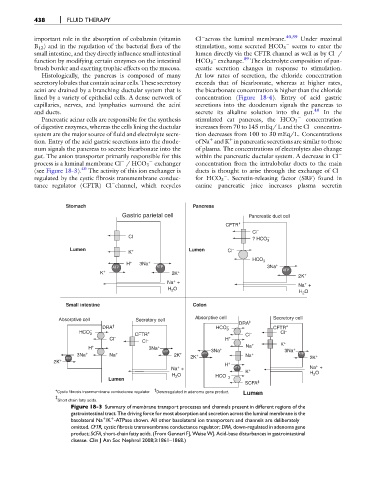
process is a luminal membrane Cl / HCO 3 exchanger concentration from the intralobular ducts to the main
(see Figure 18-3). 40 The activity of this ion exchanger is ducts is thought to arise through the exchange of Cl
regulated by the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conduc- for HCO 3 . Secretin-releasing factor (SRF) found in
tance regulator (CFTR) Cl channel, which recycles canine pancreatic juice increases plasma secretin
Stomach Pancreas
Gastric parietal cell Pancreatic duct cell
CFTR*
Cl −
Cl − −
? HCO 3
Lumen Lumen Cl −
K +
−
HCO 3
+
+
H 3Na +
ATP ATP 3Na
K + 2K + ATP
2K +
+
Na + +
Na +
H 2 O
H 2 O
Small intestine Colon
Absorptive cell Secretory cell Absorptive cell DRA ‡ Secretory cell
DRA † − CFTR*
− HCO 3 −
HCO 3 CFTR* Cl − Cl
− +
Cl − H
Cl K +
H + 3Na + 3Na + Na + 3Na +
3Na + Na + ATP 2K + + ATP Na + ATP
ATP 2K 2K +
2K + +
H +
+
Na + ATP K + Na +
H 2 O − H 2 O
Lumen HCO 3
SCFA ‡
†
*Cystic fibrosis trasnmembrane conductance regulator. Downregulated in adenoma gene product. Lumen
‡
Short chain fatty acids.
Figure 18-3 Summary of membrane transport processes and channels present in different regions of the
gastrointestinal tract. The driving force for most absorption and secretion across the luminal membrane is the
basolateral Na /K -ATPase shown. All other basolateral ion transporters and channels are deliberately
þ
þ
omitted. CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; DRA, down-regulated in adenoma gene
product; SCFA, short-chain fatty acids. (From Gennari FJ, Weise WJ. Acid-base disturbances in gastrointestinal
disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2008;3:1861–1868.)