Page 1138 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 1138
1104 Chapter 11
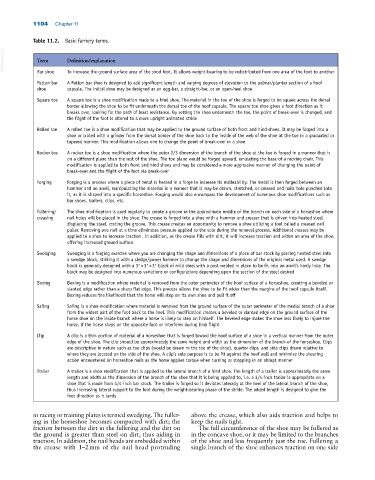
Table 11.2. Basic farriery terms.
VetBooks.ir Term Definition/explanation
Bar shoe
To increase the ground surface area of the shod foot. It allows weight‐bearing to be redistributed from one area of the foot to another
Patton bar A Patton bar shoe is designed to add significant length and varying degrees of elevation to the palmar/plantar section of a hoof
shoe capsule. The initial shoe may be designed as an egg‐bar, a straight‐bar, or an open‐heel shoe
Square toe A square toe is a shoe modification made to a hind shoe. The material in the toe of the shoe is forged to be square across the dorsal
border allowing the shoe to be fit underneath the dorsal toe of the hoof capsule. The square toe shoe gives a foot direction as it
breaks over, looking for the path of least resistance. By setting the shoe underneath the toe, the point of break‐over is changed, and
the flight of the foot is altered to a more upright animated stride
Rolled toe A rolled toe is a shoe modification that may be applied to the ground surface of both front and hind shoes. It may be forged into a
shoe or crated with a grinder from the dorsal border of the shoe back to the inside of the web of the shoe at the toe in a graduated or
tapered manner. This modification allows one to change the point of break‐over in a shoe
Rocker toe A rocker toe is a shoe modification where the outer 2/3 dimension of the branch of the shoe at the toe is forged in a manner that is
on a different plane than the rest of the shoe. The toe plane would be forged upward, emulating the base of a rocking chair. This
modification is applied to both front and hind shoes and may be considered a more aggressive manner of changing the paint of
break‐over and the flight of the foot via break‐over
Forging Forging is a process where a piece of metal is heated in a forge to increase its malleability. The metal is then forged between an
hammer and an anvil, manipulating the material in a manner that it may be drawn, stretched, or creased and nails hole punched into
it, as it is shaped into a specific horseshoe. Forging would also encompass the development of numerous shoe modifications such as
bar shoes, trailers, clips, etc.
Fullering/ The shoe modification is used regularly to create a groove in the approximate middle of the branch on each side of a horseshoe where
creasing nail holes will be placed in the shoe. The crease is forged into a shoe with a hammer and creaser that is driven into heated steel
displacing the steel, crating the groove. This crease creates an opportunity to remove a shoe utilizing a tool called a creased nail
puller. Removing one nail at a time eliminates pressure applied to the sole during the removal process. Additional creases may be
applied to a shoe to increase traction. In addition, as the crease fills with dirt, it will increase traction and widen an area of the shoe,
offering increased ground surface
Swedging Swedging is a forging exercise where you are changing the shape and dimensions of a piece of bar stock by placing heated steel into
a swedge block, striking it with a sledge/power hammer to change the shape and dimensions of the original metal used. A swedge
block is generally designed with a 3″ × 3″ × 3″ block of mild steel with a post welded in place to be fit into an anvil’s hardy hole. The
block may be designed into numerous variations or configurations depending upon the section of the steel desired
Boxing Boxing is a modification where material is removed from the outer perimeter of the hoof surface of a horseshoe, creating a beveled or
slanted edge rather than a sharp flat edge. This process allows the shoe to be fit wider than the margins of the hoof capsule itself.
Boxing reduces the likelihood that the horse will step on its own shoe and pull it off
Safing Safing is a shoe modification where material is removed from the ground surface of the outer perimeter of the medial branch of a shoe
from the widest part of the foot back to the heel. This modification creates a beveled or slanted edge on the ground surface of the
horse shoe on the inside branch where a horse is likely to step on himself. The beveled edge makes the shoe less likely to injure the
horse, if the horse steps on the opposite foot or interferes during limb flight
Clip A clip is a thin portion of material of a horseshoe that is forged toward the hoof surface of a shoe in a vertical manner from the outer
edge of the shoe. The clip should be approximately the same height and width as the dimension of the branch of the horseshoe. Clips
are descriptive in nature such as toe clips (would be drawn in the toe of the shoe), quarter clips, and side clips drawn relative to
where they are located on the side of the shoe. A clip’s sole purpose is to be fit against the hoof wall and minimize the shearing
action encountered on horseshoe nails as the horse applies torque when turning or stopping in an abrupt manner
Trailer A trailer is a shoe modification that is applied to the lateral branch of a hind shoe. The length of a trailer is approximately the same
length and width as the dimension of the branch of the shoe that it is being applied to, i.e. a 3/4‐inch trailer is appropriate on a
shoe that is made from 3/4‐inch bar stock. The trailer is forged so it deviates laterally at the heel of the lateral branch of the shoe,
thus increasing lateral support to the foot during the weight‐bearing phase of the stride. The added length is designed to give the
foot direction as it lands
in racing or training plates is termed swedging. The fuller above the crease, which also aids traction and helps to
ing in the horseshoe becomes compacted with dirt; the keep the nails tight.
friction between the dirt in the fullering and the dirt on The full circumference of the shoe may be fullered as
the ground is greater than steel on dirt, thus aiding in in the concave shoe, or it may be limited to the branches
traction. In addition, the nail heads are embedded within of the shoe and less frequently just the toe. Fullering a
the crease with 1–2 mm of the nail head protruding single branch of the shoe enhances traction on one side