Page 1180 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 1180
1146 Chapter 12
VetBooks.ir
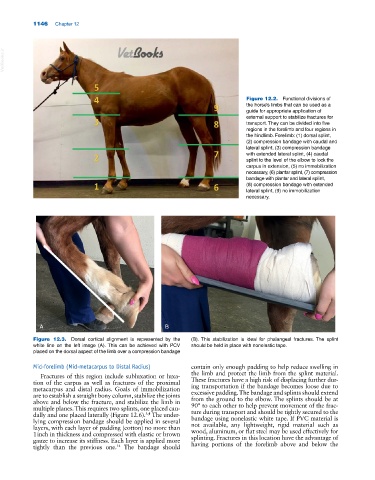
Figure 12.2. Functional divisions of
the horse’s limbs that can be used as a
guide for appropriate application of
external support to stabilize fractures for
transport. They can be divided into five
regions in the forelimb and four regions in
the hindlimb. Forelimb: (1) dorsal splint,
(2) compression bandage with caudal and
lateral splint, (3) compression bandage
with extended lateral splint, (4) caudal
splint to the level of the elbow to lock the
carpus in extension, (5) no immobilization
necessary, (6) plantar splint, (7) compression
bandage with plantar and lateral splint,
(8) compression bandage with extended
lateral splint, (9) no immobilization
necessary.
A B
Figure 12.3. Dorsal cortical alignment is represented by the (B). This stabilization is ideal for phalangeal fractures. The splint
white line on the left image (A). This can be achieved with PCV should be held in place with nonelastic tape.
placed on the dorsal aspect of the limb over a compression bandage
Mid‐forelimb (Mid‐metacarpus to Distal Radius) contain only enough padding to help reduce swelling in
Fractures of this region include subluxation or luxa the limb and protect the limb from the splint material.
tion of the carpus as well as fractures of the proximal These fractures have a high risk of displacing further dur
metacarpus and distal radius. Goals of immobilization ing transportation if the bandage becomes loose due to
are to establish a straight bony column, stabilize the joints excessive padding. The bandage and splints should extend
above and below the fracture, and stabilize the limb in from the ground to the elbow. The splints should be at
multiple planes. This requires two splints, one placed cau 90° to each other to help prevent movement of the frac
dally and one placed laterally (Figure 12.6). The under ture during transport and should be tightly secured to the
3,4
lying compression bandage should be applied in several bandage using nonelastic white tape. If PVC material is
layers, with each layer of padding (cotton) no more than not available, any lightweight, rigid material such as
1 inch in thickness and compressed with elastic or brown wood, aluminum, or flat steel may be used effectively for
gauze to increase its stiffness. Each layer is applied more splinting. Fractures in this location have the advantage of
tightly than the previous one. The bandage should having portions of the forelimb above and below the
14