Page 346 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 346
312 Chapter 3
VetBooks.ir
B
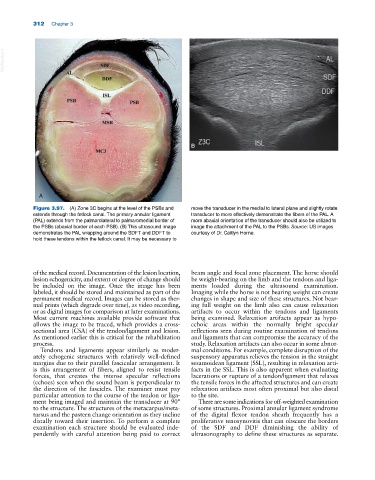
A
Figure 3.97. (A) Zone 3C begins at the level of the PSBs and move the transducer in the medial to lateral plane and slightly rotate
extends through the fetlock canal. The primary annular ligament transducer to more effectively demonstrate the fibers of the PAL. A
(PAL) extends from the palmarolateral to palmaromedial border of more abaxial orientation of the transducer should also be utilized to
the PSBs (abaxial border of each PSB). (B) This ultrasound image image the attachment of the PAL to the PSBs. Source: US images
demonstrates the PAL wrapping around the SDFT and DDFT to courtesy of Dr. Caitlyn Horne.
hold these tendons within the fetlock canal. It may be necessary to
of the medical record. Documentation of the lesion location, beam angle and focal zone placement. The horse should
lesion echogenicity, and extent or degree of change should be weight‐bearing on the limb and the tendons and liga
be included on the image. Once the image has been ments loaded during the ultrasound examination.
labeled, it should be stored and maintained as part of the Imaging while the horse is not bearing weight can create
permanent medical record. Images can be stored as ther changes in shape and size of these structures. Not bear
mal prints (which degrade over time), as video recording, ing full weight on the limb also can cause relaxation
or as digital images for comparison at later examinations. artifacts to occur within the tendons and ligaments
Most current machines available provide software that being examined. Relaxation artifacts appear as hypo
allows the image to be traced, which provides a cross‐ echoic areas within the normally bright specular
sectional area (CSA) of the tendon/ligament and lesion. reflections seen during routine examination of tendons
As mentioned earlier this is critical for the rehabilitation and ligaments that can compromise the accuracy of the
process. study. Relaxation artifacts can also occur in some abnor
Tendons and ligaments appear similarly as moder mal conditions. For example, complete disruption of the
ately echogenic structures with relatively well‐defined suspensory apparatus relieves the tension in the straight
margins due to their parallel fascicular arrangement. It sesamoidean ligament (SSL), resulting in relaxation arti
is this arrangement of fibers, aligned to resist tensile facts in the SSL. This is also apparent when evaluating
forces, that creates the intense specular reflections lacerations or rupture of a tendon/ligament that relaxes
(echoes) seen when the sound beam is perpendicular to the tensile forces in the affected structures and can create
the direction of the fascicles. The examiner must pay relaxation artifacts most often proximal but also distal
particular attention to the course of the tendon or liga to the site.
ment being imaged and maintain the transducer at 90° There are some indications for off‐weighted examination
to the structure. The structures of the metacarpus/meta of some structures. Proximal annular ligament syndrome
tarsus and the pastern change orientation as they incline of the digital flexor tendon sheath frequently has a
distally toward their insertion. To perform a complete proliferative tenosynovitis that can obscure the borders
examination each structure should be evaluated inde of the SDF and DDF diminishing the ability of
pendently with careful attention being paid to correct ultrasonography to define these structures as separate.