Page 1968 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 1968
Tooth Resorption 983
VetBooks.ir Diseases and Disorders
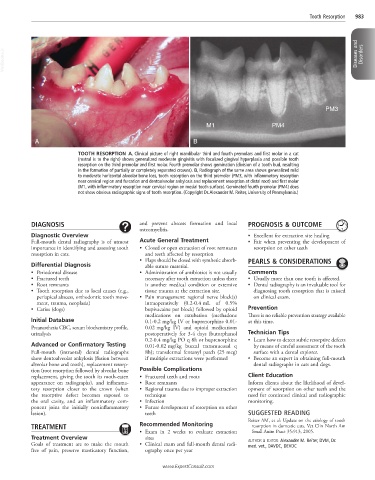
PM3
M1 PM4
A B
TOOTH RESORPTION A, Clinical picture of right mandibular third and fourth premolars and first molar in a cat
(rostral is to the right) shows generalized moderate gingivitis with focalized gingival hyperplasia and possible tooth
resorption on the third premolar and first molar. Fourth premolar shows gemination (division of a tooth bud, resulting
in the formation of partially or completely separated crowns). B, Radiograph of the same area shows generalized mild
to moderate horizontal alveolar bone loss, tooth resorption on the third premolar (PM3, with inflammatory resorption
near cervical region and furcation and dentoalveolar ankylosis and replacement resorption at distal root) and first molar
(M1, with inflammatory resorption near cervical region on mesial tooth surface). Geminated fourth premolar (PM4) does
not show obvious radiographic signs of tooth resorption. (Copyright Dr. Alexander M. Reiter, University of Pennsylvania.)
DIAGNOSIS and prevent abscess formation and local PROGNOSIS & OUTCOME
osteomyelitis.
Diagnostic Overview • Excellent for extraction site healing
Full-mouth dental radiography is of utmost Acute General Treatment • Fair when preventing the development of
importance in identifying and assessing tooth • Closed or open extraction of root remnants resorption on other teeth
resorption in cats. and teeth affected by resorption
• Flaps should be closed with synthetic absorb- PEARLS & CONSIDERATIONS
Differential Diagnosis able suture material.
• Periodontal disease • Administration of antibiotics is not usually Comments
• Fractured teeth necessary after tooth extraction unless there • Usually more than one tooth is affected.
• Root remnants is another medical condition or extensive • Dental radiography is an invaluable tool for
• Tooth resorption due to local causes (e.g., tissue trauma at the extraction site. diagnosing tooth resorption that is missed
periapical abscess, orthodontic tooth move- • Pain management: regional nerve block(s) on clinical exam.
ment, trauma, neoplasia) intraoperatively (0.2-0.4 mL of 0.5%
• Caries (dogs) bupivacaine per block) followed by opioid Prevention
medications on extubation (methadone There is no reliable prevention strategy available
Initial Database 0.1-0.2 mg/kg IV or buprenorphine 0.01- at this time.
Preanesthesia CBC, serum biochemistry profile, 0.02 mg/kg IV) and opioid medications
urinalysis postoperatively for 3-4 days (butorphanol Technician Tips
0.2-0.4 mg/kg PO q 8h or buprenorphine • Learn how to detect subtle resorptive defects
Advanced or Confirmatory Testing 0.01-0.02 mg/kg buccal transmucosal q by means of careful assessment of the tooth
Full-mouth (intraoral) dental radiographs 8h); transdermal fentanyl patch (25 mcg) surface with a dental explorer.
show dentoalveolar ankylosis (fusion between if multiple extractions were performed • Become an expert in obtaining full-mouth
alveolar bone and tooth), replacement resorp- dental radiographs in cats and dogs.
tion (root resorption followed by alveolar bone Possible Complications
replacement, giving the tooth its moth-eaten • Fractured teeth and roots Client Education
appearance on radiographs), and inflamma- • Root remnants Inform clients about the likelihood of devel-
tory resorption closer to the crown (when • Regional trauma due to improper extraction opment of resorption on other teeth and the
the resorptive defect becomes exposed to technique need for continued clinical and radiographic
the oral cavity, and an inflammatory com- • Infection monitoring.
ponent joins the initially noninflammatory • Future development of resorption on other
lesion). teeth SUGGESTED READING
Reiter AM, et al: Update on the etiology of tooth
TREATMENT Recommended Monitoring resorption in domestic cats. Vet Clin North Am
• Exam in 2 weeks to evaluate extraction Small Anim Pract 35:913, 2005.
Treatment Overview sites
Goals of treatment are to make the mouth • Clinical exam and full-mouth dental radi- AUTHOR & EDITOR: Alexander M. Reiter, DVM, Dr.
med. vet., DAVDC, DEVDC
free of pain, preserve masticatory function, ography once per year
www.ExpertConsult.com