Page 1963 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 1963
Tooth Displacement Injuries 980.e3
PEARLS & CONSIDERATIONS
VetBooks.ir Comments Diseases and Disorders
• Tooth luxation and avulsion are dental
emergencies. Immediate repositioning/
reimplantation and splinting are mandatory
for successful treatment.
• Severed pulp tissue may survive for 2 hours in
an extraoral environment. Periodontal fibers
survive 30 minutes if dry and 1-3 hours if
kept moistened.
• In most instances, endodontic treatment is
necessary after repositioning/reimplantation.
• Displaced deciduous teeth should be
extracted rather than replanted.
• Extraction of displaced permanent teeth is an
alternative to repositioning/reimplantation.
A
Technician Tips
• Technicians should bring to the veterinary’s
attention any abnormal mobility of teeth
noticed during dental charting, particularly
in trauma cases.
• Technicians should be aware about the fact
that displaced teeth need gentle handling
and use of proper flushing solutions to
avoid further damage to periodontal and
endodontic tissues.
Client Education
• Recommend soft diet and daily oral hygiene
when an oral splint is in place.
• Discuss the need for endodontic treatment,
radiographic follow-up exams, and possible
complications before tooth replantation is
B performed.
SUGGESTED READING
Gracis M: Management of periodontal trauma. In
Verstraete FJM, et al, editors: Oral and maxillo-
facial surgery in dogs and cats, Edinburgh, 2012,
Saunders, pp 201-215.
ADDITIONAL SUGGESTED
READINGS
Andreasen JO, et al: Textbook and color atlas of
traumatic injuries to the teeth, ed 4. Ames, IA,
2007, Wiley-Blackwell,.
Buffa EA, et al: The effects of wound lavage solutions
on canine fibroblasts: an in vitro study. Vet Surg
26:460-466, 1997.
Chen H, et al: The effect of intracanal anti-inflammatory
medicaments on external root resorption of replanted
dog teeth after extended extra-oral dry time. Dent
C Traumatol 24:74-78, 2008.
Hinckfuss SE, et al: An evidence-based assessment of
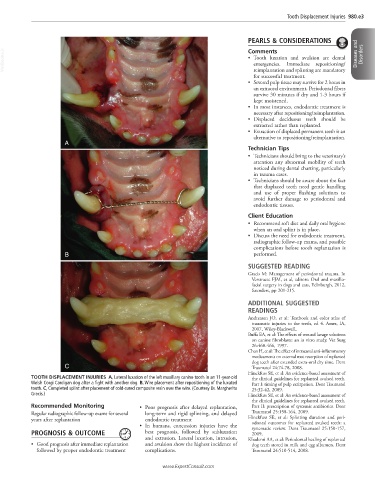
TOOTH DISPLACEMENT INJURIES A, Lateral luxation of the left maxillary canine tooth in an 11-year-old the clinical guidelines for replanted avulsed teeth.
Welsh Corgi Cardigan dog after a fight with another dog. B, Wire placement after repositioning of the luxated Part I: timing of pulp extirpation. Dent Traumatol
tooth. C, Completed splint after placement of cold-cured composite resin over the wire. (Courtesy Dr. Margherita 25:32-42, 2009.
Gracis.) Hinckfuss SE, et al: An evidence-based assessment of
the clinical guidelines for replanted avulsed teeth.
Recommended Monitoring • Poor prognosis after delayed replantation, Part II: prescription of systemic antibiotics. Dent
Regular radiographic follow-up exams for several long-term and rigid splinting, and delayed Traumatol 25:158-164, 2009.
years after replantation endodontic treatment Hinckfuss SE, et al: Splinting duration and peri-
• In humans, concussion injuries have the odontal outcomes for replanted avulsed teeth: a
systematic review. Dent Traumatol 25:150-157,
PROGNOSIS & OUTCOME best prognosis, followed by subluxation 2009.
and extrusion. Lateral luxation, intrusion, Khademi AA, et al: Periodontal healing of replanted
• Good prognosis after immediate replantation and avulsion show the highest incidence of dog teeth stored in milk and egg albumen. Dent
followed by proper endodontic treatment complications. Traumatol 24:510-514, 2008.
www.ExpertConsult.com