Page 1011 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 1011
CHAPTER 55 Clinical Conditions of the Bitch and Queen 983
often unrewarding because of the refractory nature of the Exploratory laparotomy with the goal of removal of resid-
ovarian remnant. In the queen, if ovulation or luteinization ual ovarian tissue confirms and resolves the problem. The
VetBooks.ir is stimulated during behavioral estrus, serum progesterone identification of residual ovarian tissue is facilitated by the
presence of active follicles or resultant corpora lutea. The cli-
levels >2.0 ng/mL are consistent with adequate coital stimu-
lation and functional luteal tissue. Serum LH is elevated in
of when progesterone is elevated. All visible ovarian tissue
ovariectomized females; it is only elevated in intact females nician should schedule the surgical procedure during estrus
during the 12 to 24 h surge. Serum Anti-Müllerian Hormone should be removed and evaluated by histopathology. If no
(AMH) assays are now commercially available, have excel- visible ovarian tissue is identified, all residual tissue at the
lent correlation with ORS in postpubertal females, and ovarian pedicles should be resected and submitted for his-
will differentiate exogenous estrogen exposure from ORS topathology. Removal of functional luteal tissue may induce
(Themmen et al., 2010). transient signs of pseudopregnancy in dogs and cats post-
Ultrasound should be used to support a diagnosis of ORS operatively. If profound, antiprolactin therapy (cabergoline
based on history, clinical signs, vaginal cytology, and serum 5 µg/kg q24h to effect) can be offered. Successful removal of
hormone tests; ultrasound also gives the surgeon guidance remnant ovarian tissue should result in cessation of clinical
(Video 55.1). Imaging should begin in a sagittal plane slightly signs of estrus.
caudolateral to the kidneys (where remnant ovarian tissue Medical therapy is often requested by clients not eager
is expected). Remnant ovarian tissue may be visible only to permit another surgical procedure. Progestational or
during the follicular phase (anechoic cystic structures) or androgenic compounds used to suppress follicular ovarian
the luteal phase (hypoechoic or isoechoic cystic structures) activity are not recommended because of undesirable side
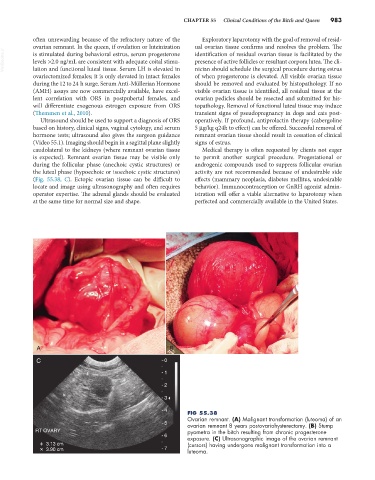
(Fig. 55.38, C). Ectopic ovarian tissue can be difficult to effects (mammary neoplasia, diabetes mellitus, undesirable
locate and image using ultrasonography and often requires behavior). Immunocontraception or GnRH agonist admin-
operator expertise. The adrenal glands should be evaluated istration will offer a viable alternative to laparotomy when
at the same time for normal size and shape. perfected and commercially available in the United States.
A B
C 0
+ 1
+ 2
+ 3
+ 4 FIG 55.38
Ovarian remnant. (A) Malignant transformation (luteoma) of an
5 ovarian remnant 8 years postovariohysterectomy. (B) Stump
RT OVARY pyometra in the bitch resulting from chronic progesterone
6 exposure. (C) Ultrasonographic image of the ovarian remnant
+ 3.13 cm (cursors) having undergone malignant transformation into a
+ 3.90 cm 7 luteoma.