Page 1124 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 1124
1096 PART IX Nervous System and Neuromuscular Disorders
exclusion; although it can be suspected based on typical sig- seizures (see Box 62.2). Focal or multifocal neurologic defi-
nalment, seizure history, and unremarkable physical, neuro- cits identified interictally strongly suggest that structural
VetBooks.ir logic, and ophthalmologic evaluations, diagnosis requires forebrain pathology exists, but not all patients with intra-
cranial disease will have an abnormal neurologic examina-
the exclusion of underlying metabolic and toxic causes
tion. Diagnosis requires careful physical, neurologic, and
through clinicopathologic testing and imaging. Intracranial
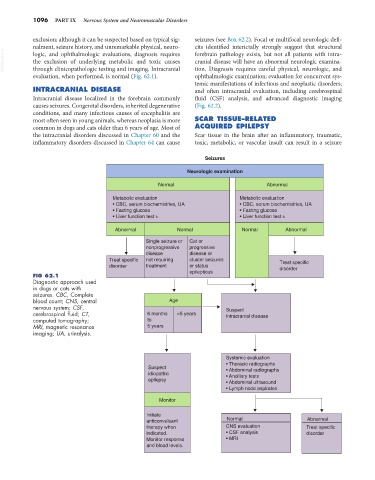
evaluation, when performed, is normal (Fig. 62.1). ophthalmologic examination; evaluation for concurrent sys-
temic manifestations of infectious and neoplastic disorders;
INTRACRANIAL DISEASE and often intracranial evaluation, including cerebrospinal
Intracranial disease localized in the forebrain commonly fluid (CSF) analysis, and advanced diagnostic imaging
causes seizures. Congenital disorders, inherited degenerative (Fig. 62.2).
conditions, and many infectious causes of encephalitis are
most often seen in young animals, whereas neoplasia is more SCAR TISSUE–RELATED
common in dogs and cats older than 6 years of age. Most of ACQUIRED EPILEPSY
the intracranial disorders discussed in Chapter 60 and the Scar tissue in the brain after an inflammatory, traumatic,
inflammatory disorders discussed in Chapter 64 can cause toxic, metabolic, or vascular insult can result in a seizure
Seizures
Neurologic examination
Normal Abnormal
Metabolic evaluation Metabolic evaluation
• CBC, serum biochemistries, UA • CBC, serum biochemistries, UA
• Fasting glucose • Fasting glucose
• Liver function test ± • Liver function test ±
Abnormal Normal Normal Abnormal
Single seizure or Cat or
nonprogressive progressive
disease disease or
Treat specific not requiring cluster seizures Treat specific
disorder treatment or status disorder
epilepticus
FIG 62.1
Diagnostic approach used
in dogs or cats with
seizures. CBC, Complete
blood count; CNS, central Age
nervous system; CSF, Suspect
cerebrospinal fluid; CT, 6 months >5 years intracranial disease
computed tomography; to
MRI, magnetic resonance 5 years
imaging; UA, urinalysis.
Systemic evaluation
• Thoracic radiographs
Suspect • Abdominal radiographs
idiopathic • Ancillary tests
epilepsy
• Abdominal ultrasound
• Lymph node aspirates
Monitor
Initiate
anticonvulsant Normal Abnormal
therapy when CNS evaluation Treat specific
indicated. • CSF analysis disorder
Monitor response • MRI
and blood levels.