Page 152 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 152
124 PART I Cardiovascular System Disorders
cusps become thicker. Mild mitral prolapse is seen early in As the LV dilates from the increasing volume overload, it
some dogs. Mitral prolapse usually involves the anterior becomes more spherical in shape. This LV enlargement and
VetBooks.ir leaflet or both leaflets. Its severity tends to increase with geometric change are associated with increased risk for CHF
and may contribute to impaired pump function. As the LV
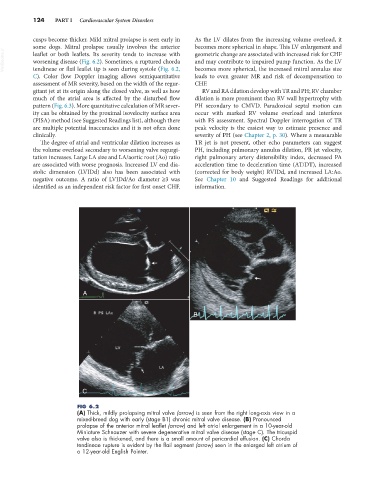
worsening disease (Fig. 6.2). Sometimes, a ruptured chorda
tendineae or flail leaflet tip is seen during systole (Fig. 6.2,
leads to even greater MR and risk of decompensation to
C). Color flow Doppler imaging allows semiquantitative becomes more spherical, the increased mitral annulus size
assessment of MR severity, based on the width of the regur- CHF.
gitant jet at its origin along the closed valve, as well as how RV and RA dilation develop with TR and PH; RV chamber
much of the atrial area is affected by the disturbed flow dilation is more prominent than RV wall hypertrophy with
pattern (Fig. 6.3). More quantitative calculation of MR sever- PH secondary to CMVD. Paradoxical septal motion can
ity can be obtained by the proximal isovelocity surface area occur with marked RV volume overload and interferes
(PISA) method (see Suggested Readings list), although there with FS assessment. Spectral Doppler interrogation of TR
are multiple potential inaccuracies and it is not often done peak velocity is the easiest way to estimate presence and
clinically. severity of PH (see Chapter 2, p. 30). Where a measurable
The degree of atrial and ventricular dilation increases as TR jet is not present, other echo parameters can suggest
the volume overload secondary to worsening valve regurgi- PH, including pulmonary annulus dilation, PR jet velocity,
tation increases. Large LA size and LA/aortic root (Ao) ratio right pulmonary artery distensibility index, decreased PA
are associated with worse prognosis. Increased LV end dia- acceleration time to deceleration time (AT/DT), increased
stolic dimension (LVIDd) also has been associated with (corrected for body weight) RVIDd, and increased LA:Ao.
negative outcome. A ratio of LVIDd/Ao diameter ≥3 was See Chapter 10 and Suggested Readings for additional
identified as an independent risk factor for first onset CHF. information.
A
B
C
FIG 6.2
(A) Thick, mildly prolapsing mitral valve (arrow) is seen from the right long-axis view in a
mixed-breed dog with early (stage B1) chronic mitral valve disease. (B) Pronounced
prolapse of the anterior mitral leaflet (arrow) and left atrial enlargement in a 10-year-old
Miniature Schnauzer with severe degenerative mitral valve disease (stage C). The tricuspid
valve also is thickened, and there is a small amount of pericardial effusion. (C) Chorda
tendineae rupture is evident by the flail segment (arrow) seen in the enlarged left atrium of
a 12-year-old English Pointer.