Page 467 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 467
CHAPTER 28 General Therapeutic Principles 439
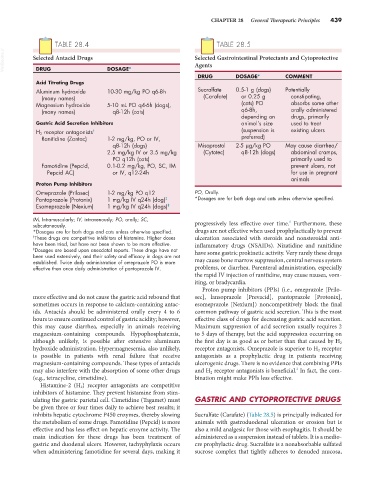
TABLE 28.4 TABLE 28.5
VetBooks.ir Selected Antacid Drugs Selected Gastrointestinal Protectants and Cytoprotective
Agents
DOSAGE*
DRUG
DRUG DOSAGE* COMMENT
Acid Titrating Drugs
Aluminum hydroxide 10-30 mg/kg PO q6-8h Sucralfate 0.5-1 g (dogs) Potentially
(many names) (Carafate) or 0.25 g constipating,
Magnesium hydroxide 5-10 mL PO q4-6h (dogs), (cats) PO absorbs some other
(many names) q8-12h (cats) q6-8h, orally administered
depending on drugs, primarily
Gastric Acid Secretion Inhibitors animal’s size used to treat
H 2 receptor antagonists † (suspension is existing ulcers
Ranitidine (Zantac) 1-2 mg/kg, PO or IV, preferred)
q8-12h (dogs) Misoprostol 2-5 µg/kg PO May cause diarrhea/
2.5 mg/kg IV or 3.5 mg/kg (Cytotec) q8-12h (dogs) abdominal cramps,
PO q12h (cats) primarily used to
Famotidine (Pepcid, 0.1-0.2 mg/kg, PO, SC, IM prevent ulcers, not
Pepcid AC) or IV, q12-24h for use in pregnant
animals
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Omeprazole (Prilosec) 1-2 mg/kg PO q12 PO, Orally.
Pantoprazole (Protonix) 1 mg/kg IV q24h (dog) ‡ *Dosages are for both dogs and cats unless otherwise specified.
Esomeprazole (Nexium) 1 mg/kg IV q24h (dogs) ‡
IM, Intramuscularly; IV, intravenously; PO, orally; SC, 1
subcutaneously. progressively less effective over time. Furthermore, these
*Dosages are for both dogs and cats unless otherwise specified. drugs are not effective when used prophylactically to prevent
† These drugs are competitive inhibitors of histamine. Higher doses ulceration associated with steroids and nonsteroidal anti-
have been tried, but have not been shown to be more effective. inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Nizatidine and ranitidine
‡ Dosages are based upon anecdotal reports. These drugs have not have some gastric prokinetic activity. Very rarely these drugs
been used extensively, and their safety and efficacy in dogs are not
established. Twice daily administration of omeprazole PO is more may cause bone marrow suppression, central nervous system
effective then once daily administration of pantoprazole IV. problems, or diarrhea. Parenteral administration, especially
the rapid IV injection of ranitidine, may cause nausea, vom-
iting, or bradycardia.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) (i.e., omeprazole [Prilo-
more effective and do not cause the gastric acid rebound that sec], lansoprazole [Prevacid], pantoprazole [Protonix],
sometimes occurs in response to calcium-containing antac- esomeprazole [Nexium]) noncompetitively block the final
ids. Antacids should be administered orally every 4 to 6 common pathway of gastric acid secretion. This is the most
hours to ensure continued control of gastric acidity; however, effective class of drugs for decreasing gastric acid secretion.
this may cause diarrhea, especially in animals receiving Maximum suppression of acid secretion usually requires 2
magnesium-containing compounds. Hypophosphatemia, to 5 days of therapy, but the acid suppression occurring on
although unlikely, is possible after extensive aluminum the first day is as good as or better than that caused by H 2
hydroxide administration. Hypermagnesemia, also unlikely, receptor antagonists. Omeprazole is superior to H 2 receptor
is possible in patients with renal failure that receive antagonists as a prophylactic drug in patients receiving
magnesium-containing compounds. These types of antacids ulcerogenic drugs. There is no evidence that combining PPIs
2
may also interfere with the absorption of some other drugs and H 2 receptor antagonists is beneficial. In fact, the com-
(e.g., tetracycline, cimetidine). bination might make PPIs less effective.
Histamine-2 (H 2 ) receptor antagonists are competitive
inhibitors of histamine. They prevent histamine from stim-
ulating the gastric parietal cell. Cimetidine (Tagamet) must GASTRIC AND CYTOPROTECTIVE DRUGS
be given three or four times daily to achieve best results; it
inhibits hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes, thereby slowing Sucralfate (Carafate) (Table 28.5) is principally indicated for
the metabolism of some drugs. Famotidine (Pepcid) is more animals with gastroduodenal ulceration or erosion but is
effective and has less effect on hepatic enzyme activity. The also a mild analgesic for those with esophagitis. It should be
main indication for these drugs has been treatment of administered as a suspension instead of tablets. It is a medio-
gastric and duodenal ulcers. However, tachyphylaxis occurs cre prophylactic drug. Sucralfate is a nonabsorbable sulfated
when administering famotidine for several days, making it sucrose complex that tightly adheres to denuded mucosa,