Page 561 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 561
CHAPTER 34 Diagnostic Tests for the Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic System 533
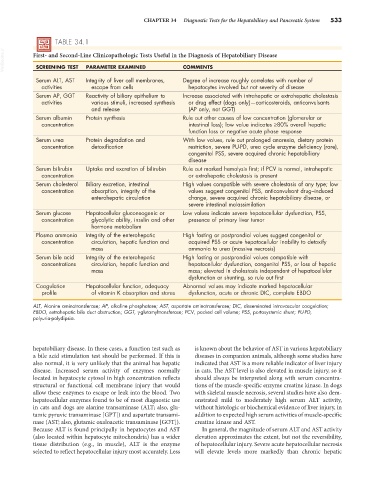
TABLE 34.1
VetBooks.ir First- and Second-Line Clinicopathologic Tests Useful in the Diagnosis of Hepatobiliary Disease
COMMENTS
PARAMETER EXAMINED
SCREENING TEST
Serum ALT, AST Integrity of liver cell membranes, Degree of increase roughly correlates with number of
activities escape from cells hepatocytes involved but not severity of disease
Serum AP, GGT Reactivity of biliary epithelium to Increase associated with intrahepatic or extrahepatic cholestasis
activities various stimuli, increased synthesis or drug effect (dogs only)—corticosteroids, anticonvulsants
and release (AP only, not GGT)
Serum albumin Protein synthesis Rule out other causes of low concentration (glomerular or
concentration intestinal loss); low value indicates ≥80% overall hepatic
function loss or negative acute phase response
Serum urea Protein degradation and With low values, rule out prolonged anorexia, dietary protein
concentration detoxification restriction, severe PU-PD, urea cycle enzyme deficiency (rare),
congenital PSS, severe acquired chronic hepatobiliary
disease
Serum bilirubin Uptake and excretion of bilirubin Rule out marked hemolysis first; if PCV is normal, intrahepatic
concentration or extrahepatic cholestasis is present
Serum cholesterol Biliary excretion, intestinal High values compatible with severe cholestasis of any type; low
concentration absorption, integrity of the values suggest congenital PSS, anticonvulsant drug–induced
enterohepatic circulation change, severe acquired chronic hepatobiliary disease, or
severe intestinal malassimilation
Serum glucose Hepatocellular gluconeogenic or Low values indicate severe hepatocellular dysfunction, PSS,
concentration glycolytic ability, insulin and other presence of primary liver tumor
hormone metabolism
Plasma ammonia Integrity of the enterohepatic High fasting or postprandial values suggest congenital or
concentration circulation, hepatic function and acquired PSS or acute hepatocellular inability to detoxify
mass ammonia to urea (massive necrosis)
Serum bile acid Integrity of the enterohepatic High fasting or postprandial values compatible with
concentrations circulation, hepatic function and hepatocellular dysfunction, congenital PSS, or loss of hepatic
mass mass; elevated in cholestasis independent of hepatocellular
dysfunction or shunting, so rule out first
Coagulation Hepatocellular function, adequacy Abnormal values may indicate marked hepatocellular
profile of vitamin K absorption and stores dysfunction, acute or chronic DIC, complete EBDO
ALT, Alanine aminotransferase; AP, alkaline phosphatase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation;
EBDO, extrahepatic bile duct obstruction; GGT, γ-glutamyltransferase; PCV, packed cell volume; PSS, portosystemic shunt; PU-PD,
polyuria-polydipsia.
hepatobiliary disease. In these cases, a function test such as is known about the behavior of AST in various hepatobiliary
a bile acid stimulation test should be performed. If this is diseases in companion animals, although some studies have
also normal, it is very unlikely that the animal has hepatic indicated that AST is a more reliable indicator of liver injury
disease. Increased serum activity of enzymes normally in cats. The AST level is also elevated in muscle injury, so it
located in hepatocyte cytosol in high concentration reflects should always be interpreted along with serum concentra-
structural or functional cell membrane injury that would tions of the muscle-specific enzyme creatine kinase. In dogs
allow these enzymes to escape or leak into the blood. Two with skeletal muscle necrosis, several studies have also dem-
hepatocellular enzymes found to be of most diagnostic use onstrated mild to moderately high serum ALT activity,
in cats and dogs are alanine transaminase (ALT; also, glu- without histologic or biochemical evidence of liver injury, in
tamic pyruvic transaminase [GPT]) and aspartate transami- addition to expected high serum activities of muscle-specific
nase (AST; also, glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase [GOT]). creatine kinase and AST.
Because ALT is found principally in hepatocytes and AST In general, the magnitude of serum ALT and AST activity
(also located within hepatocyte mitochondria) has a wider elevation approximates the extent, but not the reversibility,
tissue distribution (e.g., in muscle), ALT is the enzyme of hepatocellular injury. Severe acute hepatocellular necrosis
selected to reflect hepatocellular injury most accurately. Less will elevate levels more markedly than chronic hepatic