Page 556 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 556
528 PART IV Hepatobiliary and Exocrine Pancreatic Disorders
JAUNDICE
VetBooks.ir (CBC, chemistry profile, urinalysis)
Physical examination
Baseline clinicopathologic testing
Moderate-to-severe regenerative anemia No, or mild nonregenerative anemia
Normal-to-high plasma protein content Normal-to-high plasma protein content
Minimally abnormal liver enzyme activities High serum AP, GGT, ALT activities
Normal-to-enlarged spleen and/or liver (variable degrees)
(generalized, smooth) Small, normal, or enlarged liver
(generalized or focal, smooth or nodular)
Hemolysis
↑Production of bilirubin Abdominal Cholestasis
effusion ↓Excretion of bile
Intravascular or extravascular;
Infectious or noninfectious Fluid
Massive hematoma resorption analysis Hepatic function testing
See Table 34-4 / Abdominocentesis
Radiography
Medical management Ultrasonography
(See Chapter 82) Exudate Transudate or / Scintigraphy
modifed transudate
Bile
peritonitis Primary hepatobiliary Secondary hepatobiliary
See Tables 35-1 See Tables 35-1
Surgery and 36-1 and 36-1
Parenchymal or mixed pattern to Primary biliary pattern to
liver-specific clinicopathologic test results clinicopathologic test results
Biopsy, bile, and/or
gallbladder mucosa
Biopsy Biopsy can be culture
postponed if: CATS DOGS
Transient extrahepatic Cholangitis Cholangitis
bile duct obstruction EBDO EBDO
CATS DOGS (e.g., pancreatitis,
Hepatic lipidosis Chronic hepatitis complex duodenitis)
Diffuse primary or Diffuse primary or Acute hepatic adverse See Chapters 35 and 36
metastatic neoplasia metastatic neoplasia drug reaction
Systemic illness with Systemic illness with
hepatic involvement hepatic involvement
See Table 35-1 See Table 36-1
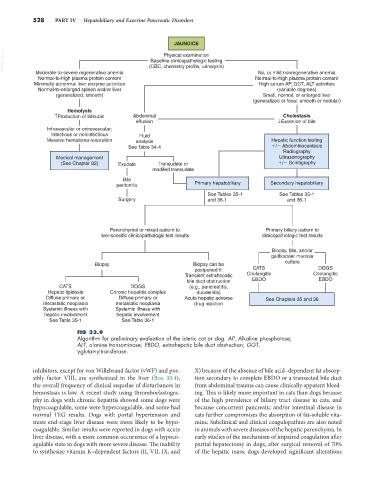
FIG 33.9
Algorithm for preliminary evaluation of the icteric cat or dog. AP, Alkaline phosphatase;
ALT, alanine transaminase; EBDO, extrahepatic bile duct obstruction; GGT,
γ-glutamyltransferase.
inhibitors, except for von Willebrand factor (vWF) and pos- X) because of the absence of bile acid–dependent fat absorp-
sibly factor VIII, are synthesized in the liver (Box 33.4), tion secondary to complete EBDO or a transected bile duct
the overall frequency of clinical sequelae of disturbances in from abdominal trauma can cause clinically apparent bleed-
hemostasis is low. A recent study using thromboelastogra- ing. This is likely more important in cats than dogs because
phy in dogs with chronic hepatitis showed some dogs were of the high prevalence of biliary tract disease in cats, and
hypocoagulable, some were hypercoagulable, and some had because concurrent pancreatic and/or intestinal disease in
normal TEG results. Dogs with portal hypertension and cats further compromises the absorption of fat-soluble vita-
more end-stage liver disease were more likely to be hypo- mins. Subclinical and clinical coagulopathies are also noted
coagulable. Similar results were reported in dogs with acute in animals with severe diseases of the hepatic parenchyma. In
liver disease, with a more common occurrence of a hypoco- early studies of the mechanism of impaired coagulation after
agulable state in dogs with more severe disease. The inability partial hepatectomy in dogs, after surgical removal of 70%
to synthesize vitamin K–dependent factors (II, VII, IX, and of the hepatic mass, dogs developed significant alterations