Page 1382 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 1382
VetBooks.ir
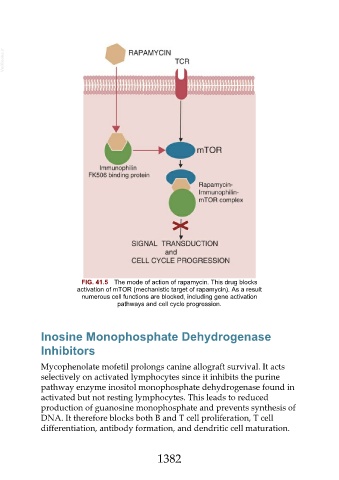
FIG. 41.5 The mode of action of rapamycin. This drug blocks
activation of mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin). As a result
numerous cell functions are blocked, including gene activation
pathways and cell cycle progression.
Inosine Monophosphate Dehydrogenase
Inhibitors
Mycophenolate mofetil prolongs canine allograft survival. It acts
selectively on activated lymphocytes since it inhibits the purine
pathway enzyme inositol monophosphate dehydrogenase found in
activated but not resting lymphocytes. This leads to reduced
production of guanosine monophosphate and prevents synthesis of
DNA. It therefore blocks both B and T cell proliferation, T cell
differentiation, antibody formation, and dendritic cell maturation.
1382