Page 1380 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 1380
VetBooks.ir
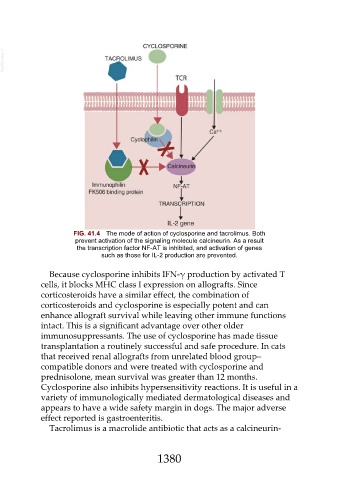
FIG. 41.4 The mode of action of cyclosporine and tacrolimus. Both
prevent activation of the signaling molecule calcineurin. As a result
the transcription factor NF-AT is inhibited, and activation of genes
such as those for IL-2 production are prevented.
Because cyclosporine inhibits IFN-γ production by activated T
cells, it blocks MHC class I expression on allografts. Since
corticosteroids have a similar effect, the combination of
corticosteroids and cyclosporine is especially potent and can
enhance allograft survival while leaving other immune functions
intact. This is a significant advantage over other older
immunosuppressants. The use of cyclosporine has made tissue
transplantation a routinely successful and safe procedure. In cats
that received renal allografts from unrelated blood group–
compatible donors and were treated with cyclosporine and
prednisolone, mean survival was greater than 12 months.
Cyclosporine also inhibits hypersensitivity reactions. It is useful in a
variety of immunologically mediated dermatological diseases and
appears to have a wide safety margin in dogs. The major adverse
effect reported is gastroenteritis.
Tacrolimus is a macrolide antibiotic that acts as a calcineurin-
1380