Page 1402 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 1402
VetBooks.ir
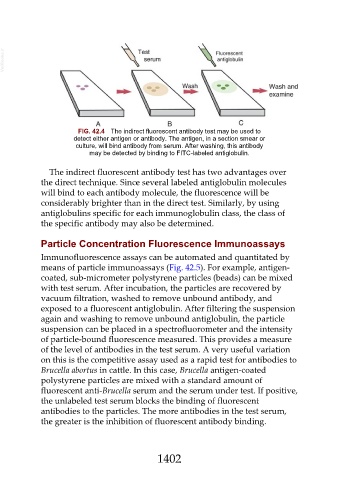
FIG. 42.4 The indirect fluorescent antibody test may be used to
detect either antigen or antibody. The antigen, in a section smear or
culture, will bind antibody from serum. After washing, this antibody
may be detected by binding to FITC-labeled antiglobulin.
The indirect fluorescent antibody test has two advantages over
the direct technique. Since several labeled antiglobulin molecules
will bind to each antibody molecule, the fluorescence will be
considerably brighter than in the direct test. Similarly, by using
antiglobulins specific for each immunoglobulin class, the class of
the specific antibody may also be determined.
Particle Concentration Fluorescence Immunoassays
Immunofluorescence assays can be automated and quantitated by
means of particle immunoassays (Fig. 42.5). For example, antigen-
coated, sub-micrometer polystyrene particles (beads) can be mixed
with test serum. After incubation, the particles are recovered by
vacuum filtration, washed to remove unbound antibody, and
exposed to a fluorescent antiglobulin. After filtering the suspension
again and washing to remove unbound antiglobulin, the particle
suspension can be placed in a spectrofluorometer and the intensity
of particle-bound fluorescence measured. This provides a measure
of the level of antibodies in the test serum. A very useful variation
on this is the competitive assay used as a rapid test for antibodies to
Brucella abortus in cattle. In this case, Brucella antigen-coated
polystyrene particles are mixed with a standard amount of
fluorescent anti-Brucella serum and the serum under test. If positive,
the unlabeled test serum blocks the binding of fluorescent
antibodies to the particles. The more antibodies in the test serum,
the greater is the inhibition of fluorescent antibody binding.
1402