Page 1403 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 1403
VetBooks.ir
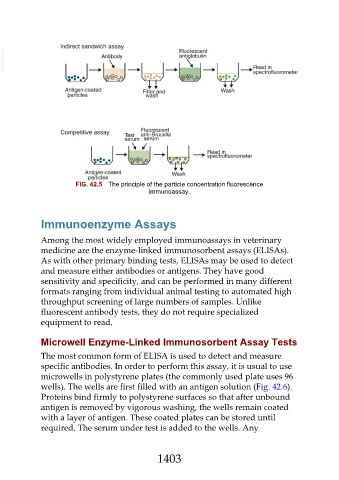
FIG. 42.5 The principle of the particle concentration fluorescence
immunoassay.
Immunoenzyme Assays
Among the most widely employed immunoassays in veterinary
medicine are the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs).
As with other primary binding tests, ELISAs may be used to detect
and measure either antibodies or antigens. They have good
sensitivity and specificity, and can be performed in many different
formats ranging from individual animal testing to automated high
throughput screening of large numbers of samples. Unlike
fluorescent antibody tests, they do not require specialized
equipment to read.
Microwell Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Tests
The most common form of ELISA is used to detect and measure
specific antibodies. In order to perform this assay, it is usual to use
microwells in polystyrene plates (the commonly used plate uses 96
wells). The wells are first filled with an antigen solution (Fig. 42.6).
Proteins bind firmly to polystyrene surfaces so that after unbound
antigen is removed by vigorous washing, the wells remain coated
with a layer of antigen. These coated plates can be stored until
required. The serum under test is added to the wells. Any
1403