Page 1408 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 1408
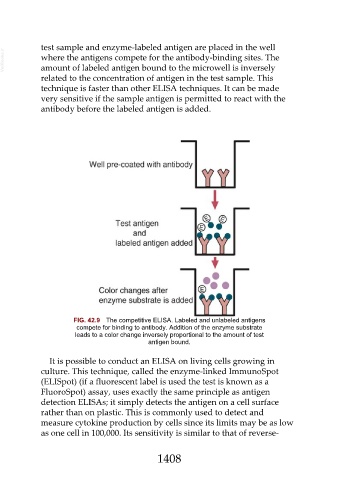
test sample and enzyme-labeled antigen are placed in the well
VetBooks.ir where the antigens compete for the antibody-binding sites. The
amount of labeled antigen bound to the microwell is inversely
related to the concentration of antigen in the test sample. This
technique is faster than other ELISA techniques. It can be made
very sensitive if the sample antigen is permitted to react with the
antibody before the labeled antigen is added.
FIG. 42.9 The competitive ELISA. Labeled and unlabeled antigens
compete for binding to antibody. Addition of the enzyme substrate
leads to a color change inversely proportional to the amount of test
antigen bound.
It is possible to conduct an ELISA on living cells growing in
culture. This technique, called the enzyme-linked ImmunoSpot
(ELISpot) (if a fluorescent label is used the test is known as a
FluoroSpot) assay, uses exactly the same principle as antigen
detection ELISAs; it simply detects the antigen on a cell surface
rather than on plastic. This is commonly used to detect and
measure cytokine production by cells since its limits may be as low
as one cell in 100,000. Its sensitivity is similar to that of reverse-
1408