Page 1480 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 1480
VetBooks.ir
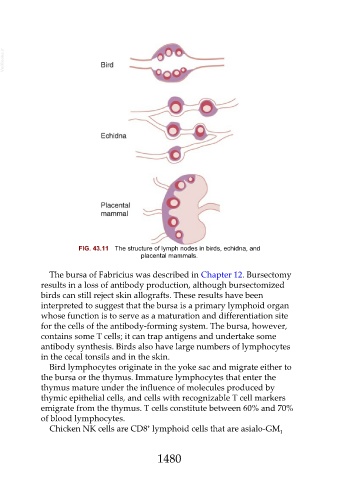
FIG. 43.11 The structure of lymph nodes in birds, echidna, and
placental mammals.
The bursa of Fabricius was described in Chapter 12. Bursectomy
results in a loss of antibody production, although bursectomized
birds can still reject skin allografts. These results have been
interpreted to suggest that the bursa is a primary lymphoid organ
whose function is to serve as a maturation and differentiation site
for the cells of the antibody-forming system. The bursa, however,
contains some T cells; it can trap antigens and undertake some
antibody synthesis. Birds also have large numbers of lymphocytes
in the cecal tonsils and in the skin.
Bird lymphocytes originate in the yoke sac and migrate either to
the bursa or the thymus. Immature lymphocytes that enter the
thymus mature under the influence of molecules produced by
thymic epithelial cells, and cells with recognizable T cell markers
emigrate from the thymus. T cells constitute between 60% and 70%
of blood lymphocytes.
+
Chicken NK cells are CD8 lymphoid cells that are asialo-GM
1
1480