Page 897 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 897
Principles of Musculoskeletal Disease 863
VetBooks.ir
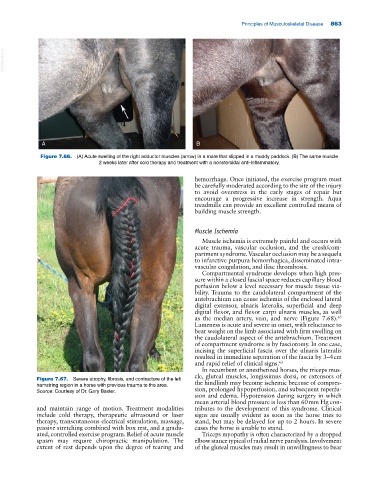
A B
Figure 7.66. (A) Acute swelling of the right adductor muscles (arrow) in a mare that slipped in a muddy paddock. (B) The same muscle
2 weeks later after cold therapy and treatment with a nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory.
hemorrhage. Once initiated, the exercise program must
be carefully moderated according to the site of the injury
to avoid overstress in the early stages of repair but
encourage a progressive increase in strength. Aqua
treadmills can provide an excellent controlled means of
building muscle strength.
Muscle Ischemia
Muscle ischemia is extremely painful and occurs with
acute trauma, vascular occlusion, and the crush/com
partment syndrome. Vascular occlusion may be a sequela
to infarctive purpura hemorrhagica, disseminated intra
vascular coagulation, and iliac thrombosis.
Compartmental syndrome develops when high pres
sure within a closed fascial space reduces capillary blood
perfusion below a level necessary for muscle tissue via
bility. Trauma to the caudolateral compartment of the
antebrachium can cause ischemia of the enclosed lateral
digital extensor, ulnaris lateralis, superficial and deep
digital flexor, and flexor carpi ulnaris muscles, as well
as the median artery, vein, and nerve (Figure 7.68).
63
Lameness is acute and severe in onset, with reluctance to
bear weight on the limb associated with firm swelling on
the caudolateral aspect of the antebrachium. Treatment
of compartment syndrome is by fasciotomy. In one case,
incising the superficial fascia over the ulnaris lateralis
resulted in immediate separation of the fascia by 3–4 cm
and rapid relief of clinical signs. 63
In recumbent or anesthetized horses, the triceps mus
cle, gluteal muscles, longissimus dorsi, or extensors of
Figure 7.67. Severe atrophy, fibrosis, and contracture of the left the hindlimb may become ischemic because of compres
hamstring region in a horse with previous trauma to the area. sion, prolonged hypoperfusion, and subsequent reperfu
Source: Courtesy of Dr. Gary Baxter.
sion and edema. Hypotension during surgery in which
mean arterial blood pressure is less than 60 mm Hg con
and maintain range of motion. Treatment modalities tributes to the development of this syndrome. Clinical
include cold therapy, therapeutic ultrasound or laser signs are usually evident as soon as the horse tries to
therapy, transcutaneous electrical stimulation, massage, stand, but may be delayed for up to 2 hours. In severe
passive stretching combined with box rest, and a gradu cases the horse is unable to stand.
ated, controlled exercise program. Relief of acute muscle Triceps myopathy is often characterized by a dropped
spasm may require chiropractic manipulation. The elbow stance typical of radial nerve paralysis. Involvement
extent of rest depends upon the degree of tearing and of the gluteal muscles may result in unwillingness to bear