Page 603 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 603
578 CHAPTER 2
VetBooks.ir bar are ideal, but these are not always available and butorphanol allows 15–20 minutes of good general
anaesthesia; a second half bolus of ketamine and xyl-
a clean empty stable is adequate when good restraint
and assistance are available.
Castrations performed in a surgical facility, under azine can be administered, providing approximately
another ten minutes of surgical time. The ‘triple drip’
general anaesthetic, are increasingly popular as they combination can also be used; the use of guafenesin
greatly reduce the complication rate and allow for a (5 or 10%) in this mixture, combined with ketamine
faster return to exercise if a closed technique is used. and xylazine, provides excellent anaesthesia and
A careful pre-operative examination of the horse muscle relaxation. Recovery is usually smooth, but
should include a physical examination and palpation the horse should be observed throughout. Applying
of the testes to ensure that they are both descended a head collar and attached lunge line allows some
into the scrotum and no gross abnormalities are control over the horse while it stands.
palpable. In younger foals the scrotum and ingui-
nal canal should be thoroughly palpated to ensure Standing castration
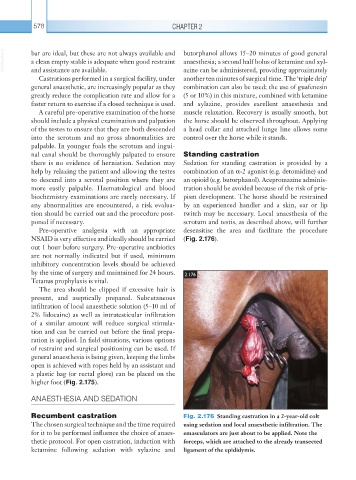
there is no evidence of herniation. Sedation may Sedation for standing castration is provided by a
help by relaxing the patient and allowing the testes combination of an α-2 agonist (e.g. detomidine) and
to descend into a scrotal position where they are an opioid (e.g. butorphanol). Acepromazine adminis-
more easily palpable. Haematological and blood tration should be avoided because of the risk of pria-
biochemistry examinations are rarely necessary. If pism development. The horse should be restrained
any abnormalities are encountered, a risk evalua- by an experienced handler and a skin, ear or lip
tion should be carried out and the procedure post- twitch may be necessary. Local anaesthesia of the
poned if necessary. scrotum and testis, as described above, will further
Pre-operative analgesia with an appropriate desensitise the area and facilitate the procedure
NSAID is very effective and ideally should be carried (Fig. 2.176).
out 1 hour before surgery. Pre-operative antibiotics
are not normally indicated but if used, minimum
inhibitory concentration levels should be achieved
by the time of surgery and maintained for 24 hours. 2.176
Tetanus prophylaxis is vital.
The area should be clipped if excessive hair is
present, and aseptically prepared. Subcutaneous
infiltration of local anaesthetic solution (5–10 ml of
2% lidocaine) as well as intratesticular infiltration
of a similar amount will reduce surgical stimula-
tion and can be carried out before the final prepa-
ration is applied. In field situations, various options
of restraint and surgical positioning can be used. If
general anaesthesia is being given, keeping the limbs
open is achieved with ropes held by an assistant and
a plastic bag (or rectal glove) can be placed on the
higher foot (Fig. 2.175).
ANAESTHESIA AND SEDATION
Recumbent castration Fig. 2.176 Standing castration in a 2-year-old colt
The chosen surgical technique and the time required using sedation and local anaesthetic infiltration. The
for it to be performed influence the choice of anaes- emasculators are just about to be applied. Note the
thetic protocol. For open castration, induction with forceps, which are attached to the already transected
ketamine following sedation with xylazine and ligament of the epididymis.