Page 605 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 605
580 CHAPTER 2
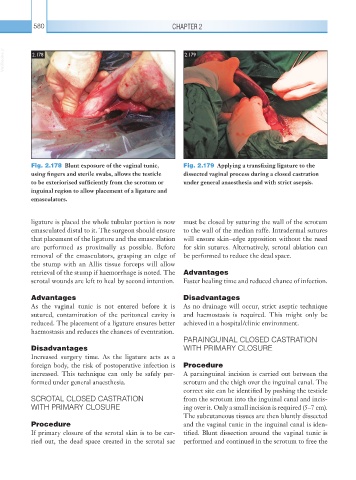
VetBooks.ir 2.178 2.179
Fig. 2.178 Blunt exposure of the vaginal tunic, Fig. 2.179 Applying a transfixing ligature to the
using fingers and sterile swabs, allows the testicle dissected vaginal process during a closed castration
to be exteriorised sufficiently from the scrotum or under general anaesthesia and with strict asepsis.
inguinal region to allow placement of a ligature and
emasculators.
ligature is placed the whole tubular portion is now must be closed by suturing the wall of the scrotum
emasculated distal to it. The surgeon should ensure to the wall of the median raffe. Intradermal sutures
that placement of the ligature and the emasculation will ensure skin–edge apposition without the need
are performed as proximally as possible. Before for skin sutures. Alternatively, scrotal ablation can
removal of the emasculators, grasping an edge of be performed to reduce the dead space.
the stump with an Allis tissue forceps will allow
retrieval of the stump if haemorrhage is noted. The Advantages
scrotal wounds are left to heal by second intention. Faster healing time and reduced chance of infection.
Advantages Disadvantages
As the vaginal tunic is not entered before it is As no drainage will occur, strict aseptic technique
sutured, contamination of the peritoneal cavity is and haemostasis is required. This might only be
reduced. The placement of a ligature ensures better achieved in a hospital/clinic environment.
haemostasis and reduces the chances of eventration.
PARAINGUINAL CLOSED CASTRATION
Disadvantages WITH PRIMARY CLOSURE
Increased surgery time. As the ligature acts as a
foreign body, the risk of postoperative infection is Procedure
increased. This technique can only be safely per- A parainguinal incision is carried out between the
formed under general anaesthesia. scrotum and the thigh over the inguinal canal. The
correct site can be identified by pushing the testicle
SCROTAL CLOSED CASTRATION from the scrotum into the inguinal canal and incis-
WITH PRIMARY CLOSURE ing over it. Only a small incision is required (5–7 cm).
The subcutaneous tissues are then bluntly dissected
Procedure and the vaginal tunic in the inguinal canal is iden-
If primary closure of the scrotal skin is to be car- tified. Blunt dissection around the vaginal tunic is
ried out, the dead space created in the scrotal sac performed and continued in the scrotum to free the