Page 254 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 254
Sense Organs / 239
The inner ear may be divided into two
functional parts. In one, the osseous laby
VetBooks.ir rinth forms a coiled, snail shell‐shaped a Vestibular
membrane
cochlea, inside of which is the cochlear
duct, a part of the membranous labyrinth. b
The cochlear duct houses the receptors for Tectorial
audition. These receptors are innervated membrane
by the cochlear division of the vestibuloc Spiral
ochlear nerve. c ganglion
The second part constitutes the vesti
bular apparatus. Within the utriculus, Basilar
sacculus, and semicircular ducts that membrane
constitute the vestibular apparatus are the
receptors that detect accelerations of the
head, including acceleration due to gravity.
Accelerations of the head contribute to
the sense of equilibrium or balance. The
vestibular apparatus is innervated by the
vestibular division of the vestibulococh
lear nerve.
Physiology of Hearing
The environmental energy detected in
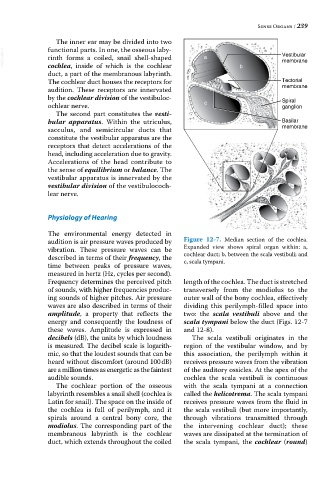
audition is air pressure waves produced by Figure 12-7. Median section of the cochlea.
vibration. These pressure waves can be Expanded view shows spiral organ within: a,
described in terms of their frequency, the cochlear duct; b, between the scala vestibuli; and
c, scala tympani.
time between peaks of pressure waves,
measured in hertz (Hz, cycles per second).
Frequency determines the perceived pitch length of the cochlea. The duct is stretched
of sounds, with higher frequencies produc transversely from the modiolus to the
ing sounds of higher pitches. Air pressure outer wall of the bony cochlea, effectively
waves are also described in terms of their dividing this perilymph‐filled space into
amplitude, a property that reflects the two: the scala vestibuli above and the
energy and consequently the loudness of scala tympani below the duct (Figs. 12‐7
these waves. Amplitude is expressed in and 12‐8).
decibels (dB), the units by which loudness The scala vestibuli originates in the
is measured. The decibel scale is logarith region of the vestibular window, and by
mic, so that the loudest sounds that can be this association, the perilymph within it
heard without discomfort (around 100 dB) receives pressure waves from the vibration
are a million times as energetic as the faintest of the auditory ossicles. At the apex of the
audible sounds. cochlea the scala vestibuli is continuous
The cochlear portion of the osseous with the scala tympani at a connection
labyrinth resembles a snail shell (cochlea is called the helicotrema. The scala tympani
Latin for snail). The space on the inside of receives pressure waves from the fluid in
the cochlea is full of perilymph, and it the scala vestibuli (but more importantly,
spirals around a central bony core, the through vibrations transmitted through
modiolus. The corresponding part of the the intervening cochlear duct); these
membranous labyrinth is the cochlear waves are dissipated at the termination of
duct, which extends throughout the coiled the scala tympani, the cochlear (round)