Page 251 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 251
236 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
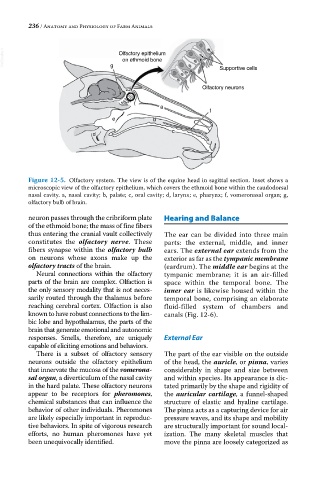
VetBooks.ir g Olfactory epithelium Supportive cells
on ethmoid bone
Olfactory neurons
a
f
e b
c
d
Figure 12-5. Olfactory system. The view is of the equine head in sagittal section. Inset shows a
microscopic view of the olfactory epithelium, which covers the ethmoid bone within the caudodorsal
nasal cavity. a, nasal cavity; b, palate; c, oral cavity; d, larynx; e, pharynx; f, vomeronasal organ; g,
olfactory bulb of brain.
neuron passes through the cribriform plate Hearing and Balance
of the ethmoid bone; the mass of fine fibers
thus entering the cranial vault collectively The ear can be divided into three main
constitutes the olfactory nerve. These parts: the external, middle, and inner
fibers synapse within the olfactory bulb ears. The external ear extends from the
on neurons whose axons make up the exterior as far as the tympanic membrane
olfactory tracts of the brain. (eardrum). The middle ear begins at the
Neural connections within the olfactory tympanic membrane; it is an air‐filled
parts of the brain are complex. Olfaction is space within the temporal bone. The
the only sensory modality that is not neces inner ear is likewise housed within the
sarily routed through the thalamus before temporal bone, comprising an elaborate
reaching cerebral cortex. Olfaction is also fluid‐filled system of chambers and
known to have robust connections to the lim canals (Fig. 12‐6).
bic lobe and hypothalamus, the parts of the
brain that generate emotional and autonomic
responses. Smells, therefore, are uniquely External Ear
capable of eliciting emotions and behaviors.
There is a subset of olfactory sensory The part of the ear visible on the outside
neurons outside the olfactory epithelium of the head, the auricle, or pinna, varies
that innervate the mucosa of the vomerona considerably in shape and size between
sal organ, a diverticulum of the nasal cavity and within species. Its appearance is dic
in the hard palate. These olfactory neurons tated primarily by the shape and rigidity of
appear to be receptors for pheromones, the auricular cartilage, a funnel‐shaped
chemical substances that can influence the structure of elastic and hyaline cartilage.
behavior of other individuals. Pheromones The pinna acts as a capturing device for air
are likely especially important in reproduc pressure waves, and its shape and mobility
tive behaviors. In spite of vigorous research are structurally important for sound local
efforts, no human pheromones have yet ization. The many skeletal muscles that
been unequivocally identified. move the pinna are loosely categorized as