Page 247 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 247
232 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
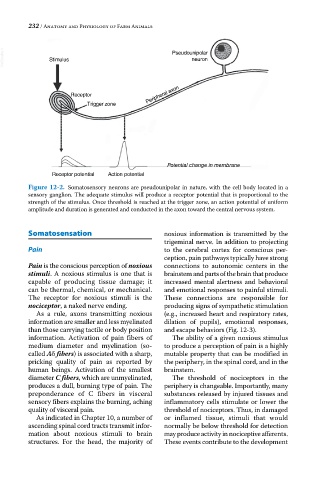
VetBooks.ir Stimulus Pseudounipolar
neuron
Peripheral axon
Receptor
Trigger zone
Potential change in membrane
Receptor potential Action potential
Figure 12-2. Somatosensory neurons are pseudounipolar in nature, with the cell body located in a
sensory ganglion. The adequate stimulus will produce a receptor potential that is proportional to the
strength of the stimulus. Once threshold is reached at the trigger zone, an action potential of uniform
amplitude and duration is generated and conducted in the axon toward the central nervous system.
Somatosensation noxious information is transmitted by the
trigeminal nerve. In addition to projecting
Pain to the cerebral cortex for conscious per
ception, pain pathways typically have strong
Pain is the conscious perception of noxious connections to autonomic centers in the
stimuli. A noxious stimulus is one that is brainstem and parts of the brain that produce
capable of producing tissue damage; it increased mental alertness and behavioral
can be thermal, chemical, or mechanical. and emotional responses to painful stimuli.
The receptor for noxious stimuli is the These connections are responsible for
nociceptor, a naked nerve ending. producing signs of sympathetic stimulation
As a rule, axons transmitting noxious (e.g., increased heart and respiratory rates,
information are smaller and less myelinated dilation of pupils), emotional responses,
than those carrying tactile or body position and escape behaviors (Fig. 12‐3).
information. Activation of pain fibers of The ability of a given noxious stimulus
medium diameter and myelination (so‐ to produce a perception of pain is a highly
called Aδ fibers) is associated with a sharp, mutable property that can be modified in
pricking quality of pain as reported by the periphery, in the spinal cord, and in the
human beings. Activation of the smallest brainstem.
diameter C fibers, which are unmyelinated, The threshold of nociceptors in the
produces a dull, burning type of pain. The periphery is changeable. Importantly, many
preponderance of C fibers in visceral substances released by injured tissues and
sensory fibers explains the burning, aching inflammatory cells stimulate or lower the
quality of visceral pain. threshold of nociceptors. Thus, in damaged
As indicated in Chapter 10, a number of or inflamed tissue, stimuli that would
ascending spinal cord tracts transmit infor normally be below threshold for detection
mation about noxious stimuli to brain may produce activity in nociceptive afferents.
structures. For the head, the majority of These events contribute to the development