Page 248 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 248
Sense Organs / 233
Cerebral cortex on which it synapses, making it respond
Conscious perception more vigorously to subsequent stimulation.
VetBooks.ir Limbic system This is called windup or spinal facilitation
of pain.
Emotional meaning
Activity in spinal nociceptive pathways
Hypothalamus and brainstem
Autonomic reflexes is also strongly influenced by descending
antinociceptive systems that originate in
the brainstem. The midbrain and medulla
both possess midline nuclei that inhibit
nociception via their connections with
nociceptive pathways. These nuclei use a
variety of neurotransmitters, most notably
PNS CNS endorphins, transmitters with powerful
antinociceptive properties.
Stoicism, an apparent indifference to
Trigeminal n. pain, is largely determined by personality
and training among both humans and
animals. High‐strung individuals may
exhibit exaggerated reactions to stimuli
Local reflex arcs that scarcely merit attention in more
“laid‐back” individuals. Interestingly,
Spinal nn. the effectiveness of applying a twitch to a
horse’s upper lip as a method of restraint
during mildly painful procedures has
long been attributed to redirecting the
horse’s attention from the procedure to
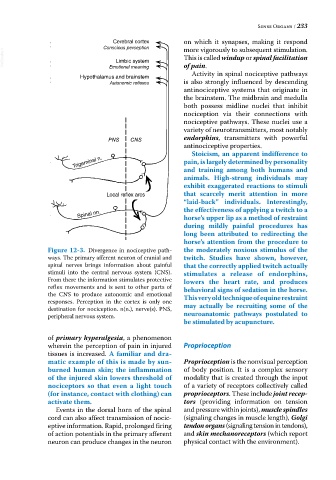
Figure 12-3. Divergence in nociceptive path the moderately noxious stimulus of the
ways. The primary afferent neuron of cranial and twitch. Studies have shown, however,
spinal nerves brings information about painful that the correctly applied twitch actually
stimuli into the central nervous system (CNS). stimulates a release of endorphins,
From there the information stimulates protective lowers the heart rate, and produces
reflex movements and is sent to other parts of
the CNS to produce autonomic and emotional behavioral signs of sedation in the horse.
responses. Perception in the cortex is only one This very old technique of equine restraint
destination for nociception. n(n.), nerve(s). PNS, may actually be recruiting some of the
peripheral nervous system. neuroanatomic pathways postulated to
be stimulated by acupuncture.
of primary hyperalgesia, a phenomenon
wherein the perception of pain in injured Proprioception
tissues is increased. A familiar and dra-
matic example of this is made by sun- Proprioception is the nonvisual perception
burned human skin; the inflammation of body position. It is a complex sensory
of the injured skin lowers threshold of modality that is created through the input
nociceptors so that even a light touch of a variety of receptors collectively called
(for instance, contact with clothing) can proprioceptors. These include joint recep
activate them. tors (providing information on tension
Events in the dorsal horn of the spinal and pressure within joints), muscle spindles
cord can also affect transmission of nocic (signaling changes in muscle length), Golgi
eptive information. Rapid, prolonged firing tendon organs (signaling tension in tendons),
of action potentials in the primary afferent and skin mechanoreceptors (which report
neuron can produce changes in the neuron physical contact with the environment).