Page 295 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 295
280 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
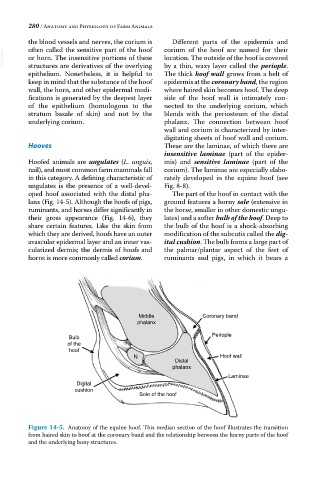
Different parts of the epidermis and
the blood vessels and nerves, the corium is corium of the hoof are named for their
often called the sensitive part of the hoof
VetBooks.ir or horn. The insensitive portions of these location. The outside of the hoof is covered
by a thin, waxy layer called the periople.
structures are derivatives of the overlying
epithelium. Nonetheless, it is helpful to The thick hoof wall grows from a belt of
keep in mind that the substance of the hoof epidermis at the coronary band, the region
wall, the horn, and other epidermal modi- where haired skin becomes hoof. The deep
fications is generated by the deepest layer side of the hoof wall is intimately con-
of the epithelium (homologous to the nected to the underlying corium, which
stratum basale of skin) and not by the blends with the periosteum of the distal
underlying corium. phalanx. The connection between hoof
wall and corium is characterized by inter-
digitating sheets of hoof wall and corium.
Hooves These are the laminae, of which there are
insensitive laminae (part of the epider-
Hoofed animals are ungulates (L. unguis, mis) and sensitive laminae (part of the
nail), and most common farm mammals fall corium). The laminae are especially elabo-
in this category. A defining characteristic of rately developed in the equine hoof (see
ungulates is the presence of a well‐devel- Fig. 8‐8).
oped hoof associated with the distal pha- The part of the hoof in contact with the
lanx (Fig. 14‐5). Although the hoofs of pigs, ground features a horny sole (extensive in
ruminants, and horses differ significantly in the horse, smaller in other domestic ungu-
their gross appearance (Fig. 14‐6), they lates) and a softer bulb of the hoof. Deep to
share certain features. Like the skin from the bulb of the hoof is a shock‐absorbing
which they are derived, hoofs have an outer modification of the subcutis called the dig-
avascular epidermal layer and an inner vas- ital cushion. The bulb forms a large part of
cularized dermis; the dermis of hoofs and the palmar/plantar aspect of the feet of
horns is more commonly called corium. ruminants and pigs, in which it bears a
Middle Coronary band
phalanx
Bulb Periople
of the
hoof
N Hoof wall
Distal
phalanx
Laminae
Digital
cushion
Sole of the hoof
Figure 14-5. Anatomy of the equine hoof. This median section of the hoof illustrates the transition
from haired skin to hoof at the coronary band and the relationship between the horny parts of the hoof
and the underlying bony structures.