Page 379 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 379
364 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
is
VetBooks.ir I
I
*
pc
II
II
is
is
I
II
am
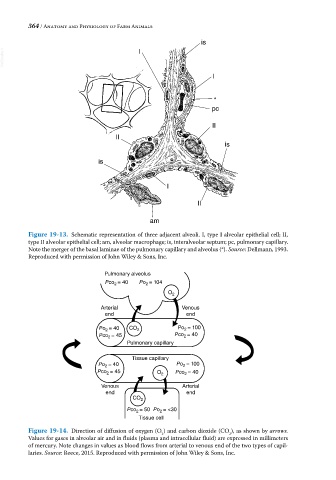
Figure 19-13. Schematic representation of three adjacent alveoli. I, type I alveolar epithelial cell; II,
type II alveolar epithelial cell; am, alveolar macrophage; is, interalveolar septum; pc, pulmonary capillary.
Note the merger of the basal laminae of the pulmonary capillary and alveolus (*). Source: Dellmann, 1993.
Reproduced with permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Pulmonary alveolus
Pco = 40 Po = 104
2
2
O 2
Arterial Venous
end end
Po = 40 CO 2 Po 2 = 100
2
= 45 = 40
Pco 2 Pco 2
Pulmonary capillary
Tissue capillary
Po = 40 Po = 100
2
2
Pco = 45 O 2 Pco = 40
2
2
Venous Arterial
end end
CO 2
Pco 2 = 50 Po 2 = <30
Tissue cell
Figure 19-14. Direction of diffusion of oxygen (O ) and carbon dioxide (CO ), as shown by arrows.
2
2
Values for gases in alveolar air and in fluids (plasma and intracellular fluid) are expressed in millimeters
of mercury. Note changes in values as blood flows from arterial to venous end of the two types of capil-
laries. Source: Reece, 2015. Reproduced with permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.