Page 431 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 431
416 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
GUT BLOOD
VetBooks.ir
Used for energy by many cells
Stored as glycogen in muscle
GLUCOSE GLUCOSE
Stored as glycogen in liver
Used for triglyceride synthesis
in the liver
Secreted by liver
as part of very low
density lipoproteins
Used for protein
AMINO ACIDS AMINO ACIDS synthesis by all cells
VLDLs
Release of free fatty
acids by lipases
Storage of fatty acids as triglycerides
TRIGLYCERIDES in adipose tissue or use by many
cells for energy
FATTY ACIDS CHYLOMICRONS
containing newly
synthesized Release of free
triglycerides fatty acids by lipases
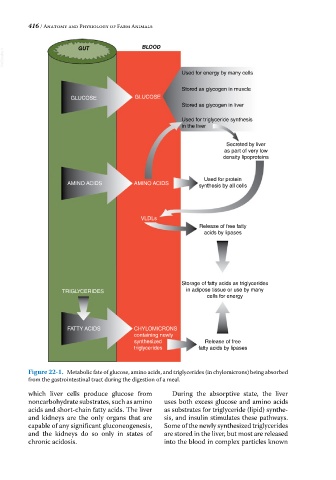
Figure 22-1. Metabolic fate of glucose, amino acids, and triglycerides (in chylomicrons) being absorbed
from the gastrointestinal tract during the digestion of a meal.
which liver cells produce glucose from During the absorptive state, the liver
noncarbohydrate substrates, such as amino uses both excess glucose and amino acids
acids and short‐chain fatty acids. The liver as substrates for triglyceride (lipid) synthe-
and kidneys are the only organs that are sis, and insulin stimulates these pathways.
capable of any significant gluconeogenesis, Some of the newly synthesized triglycerides
and the kidneys do so only in states of are stored in the liver, but most are released
chronic acidosis. into the blood in complex particles known