Page 433 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 433
418 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
VetBooks.ir LIVER BLOOD ADIPOSE
TISSUE
Glucose
Glycogen Glucose for Triglycerides
energy
Glyconeogenesis
Fatty acids
Fatty acids
Ketones
SKELETAL MUSCLE
Ketones
(also used by
other cells for ENERGY
energy)
Glycogen Glucose
Amino acids Amino Protein
acids
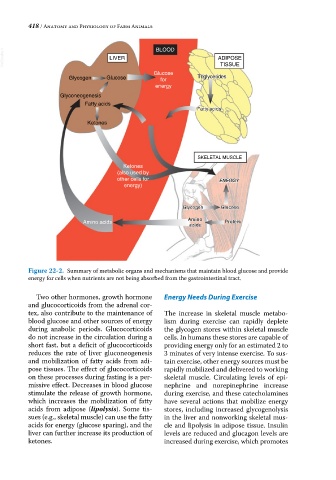
Figure 22-2. Summary of metabolic organs and mechanisms that maintain blood glucose and provide
energy for cells when nutrients are not being absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Two other hormones, growth hormone Energy Needs During Exercise
and glucocorticoids from the adrenal cor-
tex, also contribute to the maintenance of The increase in skeletal muscle metabo-
blood glucose and other sources of energy lism during exercise can rapidly deplete
during anabolic periods. Glucocorticoids the glycogen stores within skeletal muscle
do not increase in the circulation during a cells. In humans these stores are capable of
short fast, but a deficit of glucocorticoids providing energy only for an estimated 2 to
reduces the rate of liver gluconeogenesis 3 minutes of very intense exercise. To sus-
and mobilization of fatty acids from adi- tain exercise, other energy sources must be
pose tissues. The effect of glucocorticoids rapidly mobilized and delivered to working
on these processes during fasting is a per- skeletal muscle. Circulating levels of epi-
missive effect. Decreases in blood glucose nephrine and norepinephrine increase
stimulate the release of growth hormone, during exercise, and these catecholamines
which increases the mobilization of fatty have several actions that mobilize energy
acids from adipose (lipolysis). Some tis- stores, including increased glycogenolysis
sues (e.g., skeletal muscle) can use the fatty in the liver and nonworking skeletal mus-
acids for energy (glucose sparing), and the cle and lipolysis in adipose tissue. Insulin
liver can further increase its production of levels are reduced and glucagon levels are
ketones. increased during exercise, which promotes